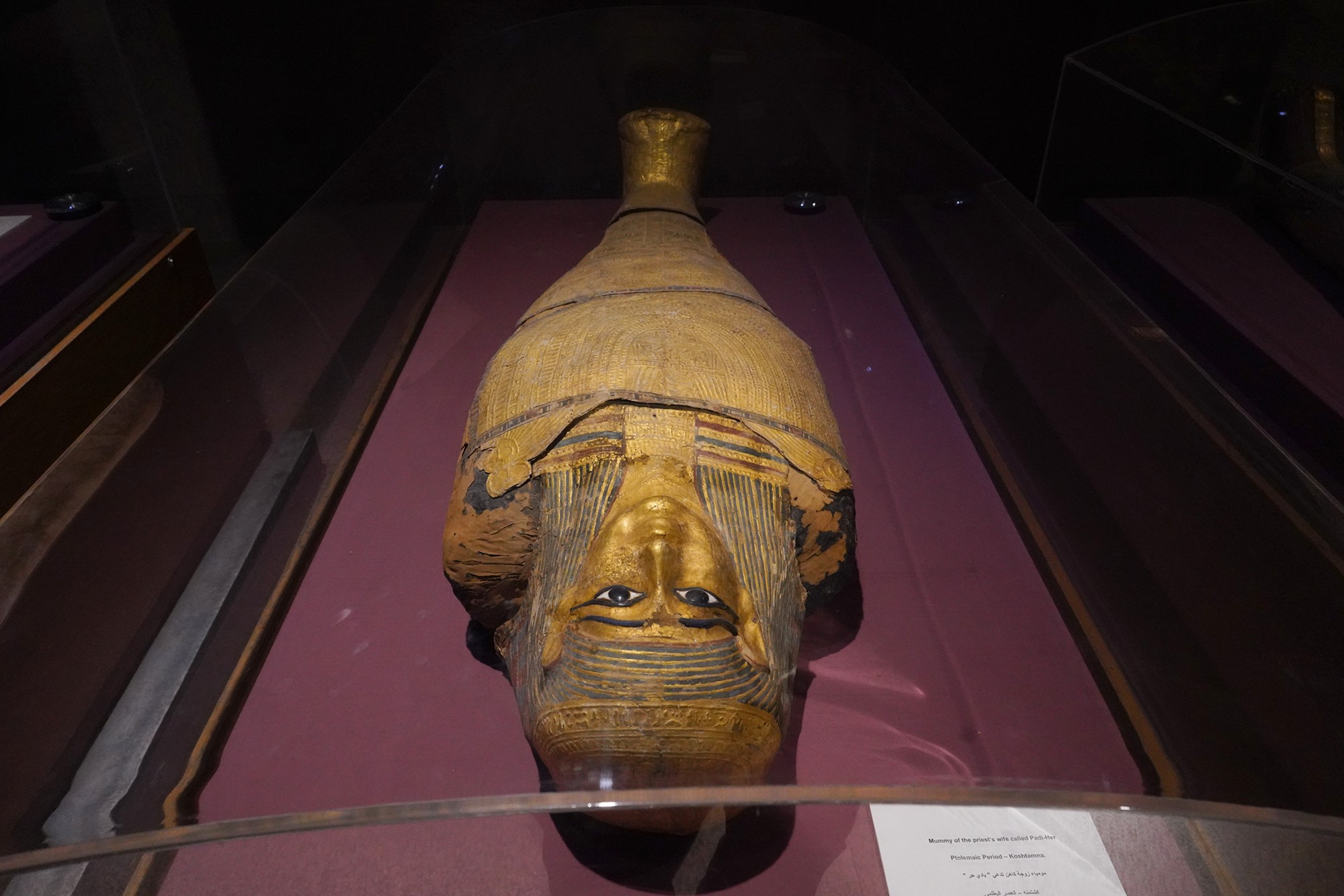
Nubian Museum, Aswan, Egypt
The Nubian Museum is located in Aswan, Egypt, and is dedicated to preserving and showcasing the history and culture of the Nubian people. 833
Nubian Museum: Assuan, Sheyakhah Oula, Aswan 1, Aswan Governorate 1240853, Egypt
Date Picture Taken: February, 2024
Nubia is a region along the Nile River that spans parts of southern Egypt and northern Sudan. The museum was established to salvage and exhibit artifacts that were at risk of being submerged due to the construction of the Aswan High Dam.



Buildings along the Nile River
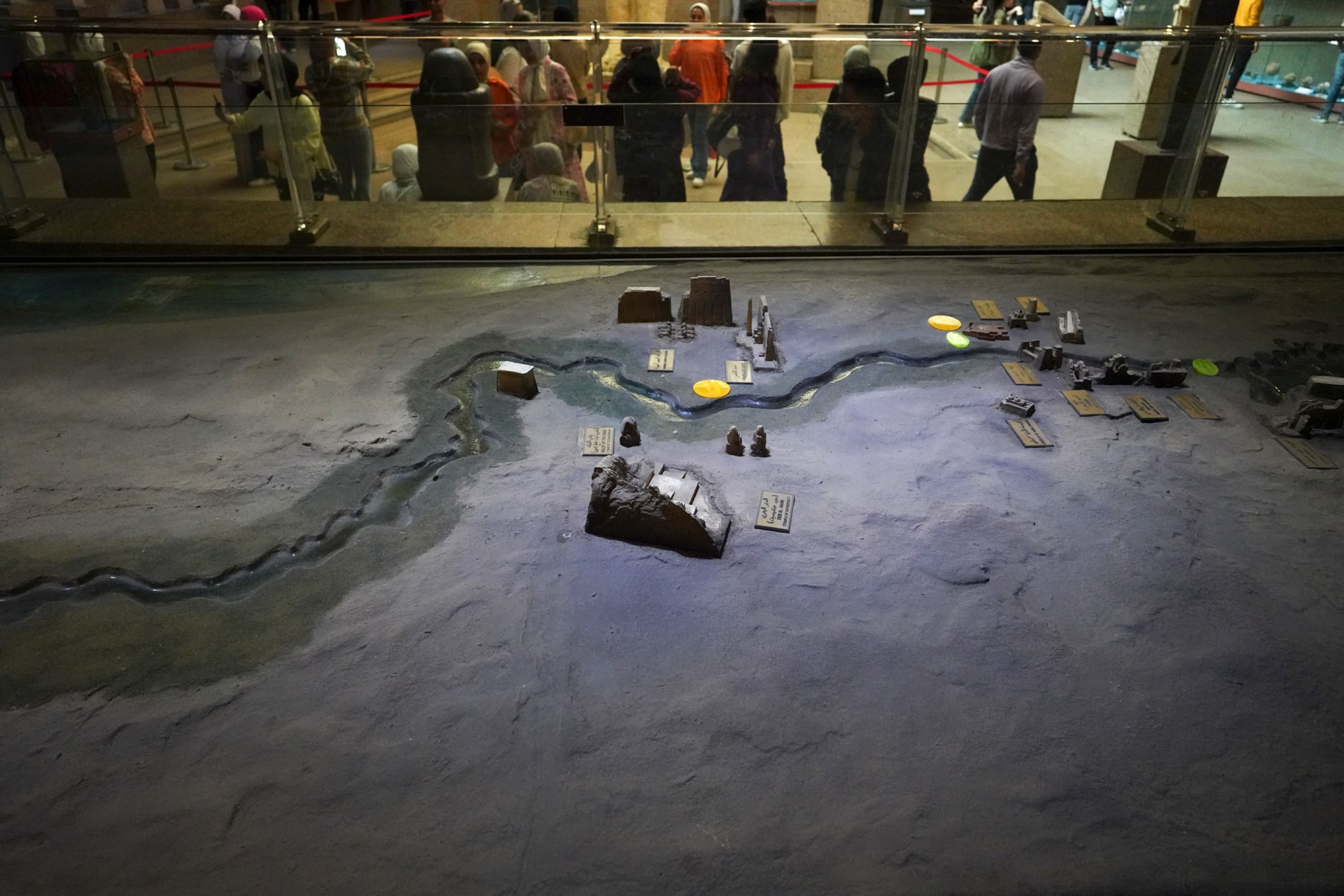
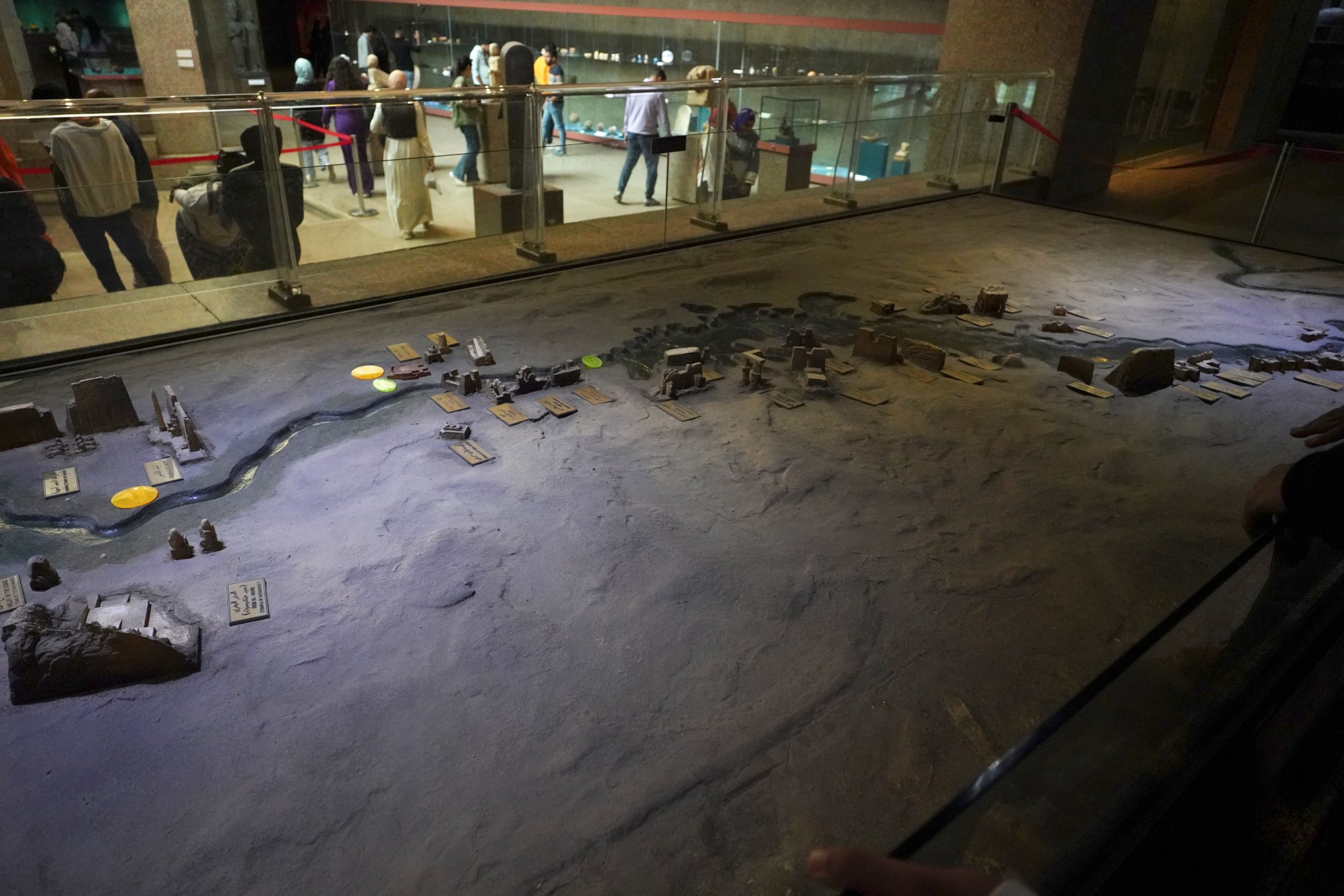
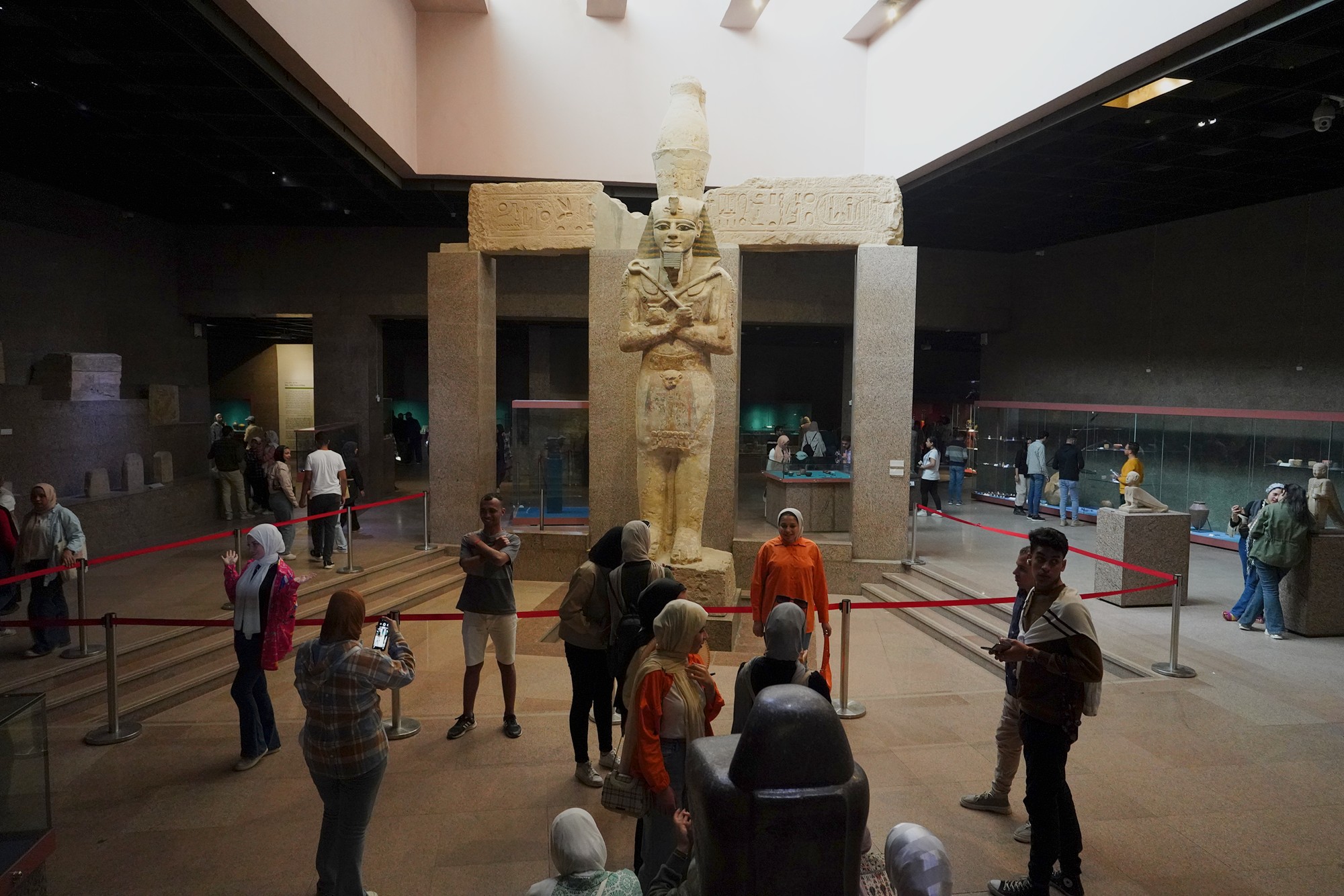



In the older times, Nubia, a region south of Aswan in Egypt, was a different country than Egypt.
“Nubian” refers to the people, culture, and region of Nubia, a historical region along the Nile River that encompasses parts of southern Egypt and northern Sudan. The Nubian people have a distinct cultural and historical identity separate from ancient Egypt, although the two civilizations interacted and influenced each other.
At present, Nubia is now a part of Egypt. The picture below shows the chronology of both Egypt and Nubia.
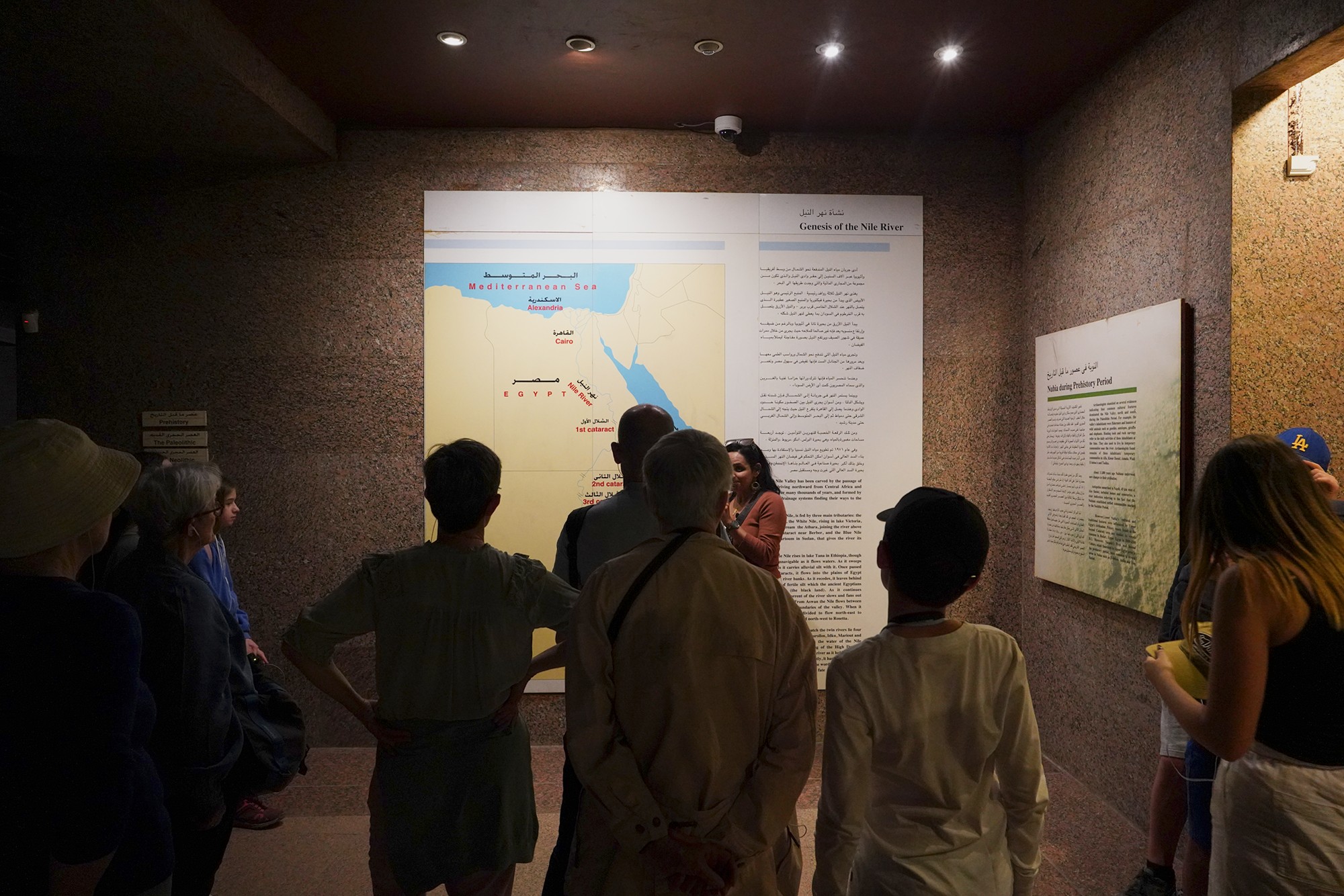
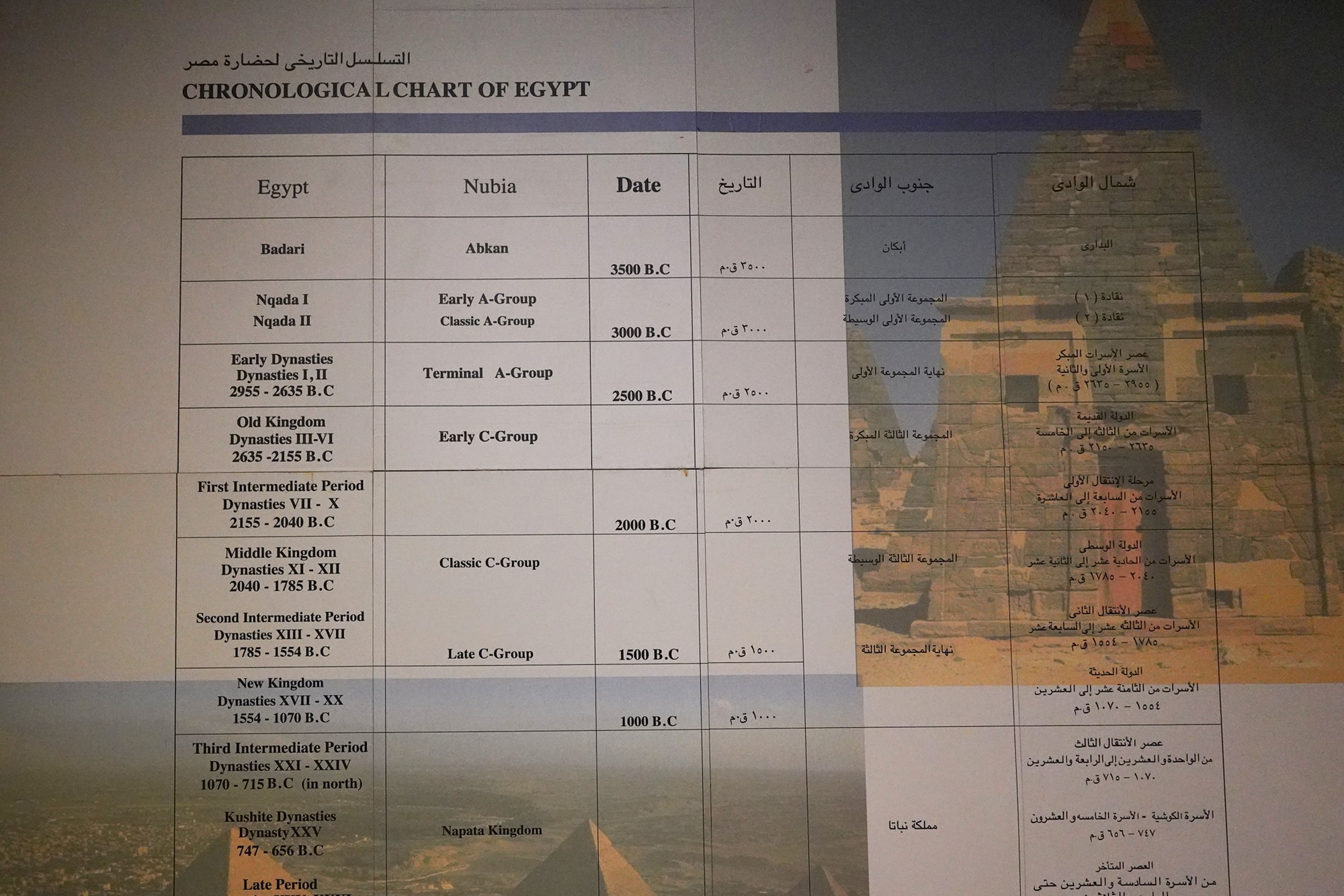

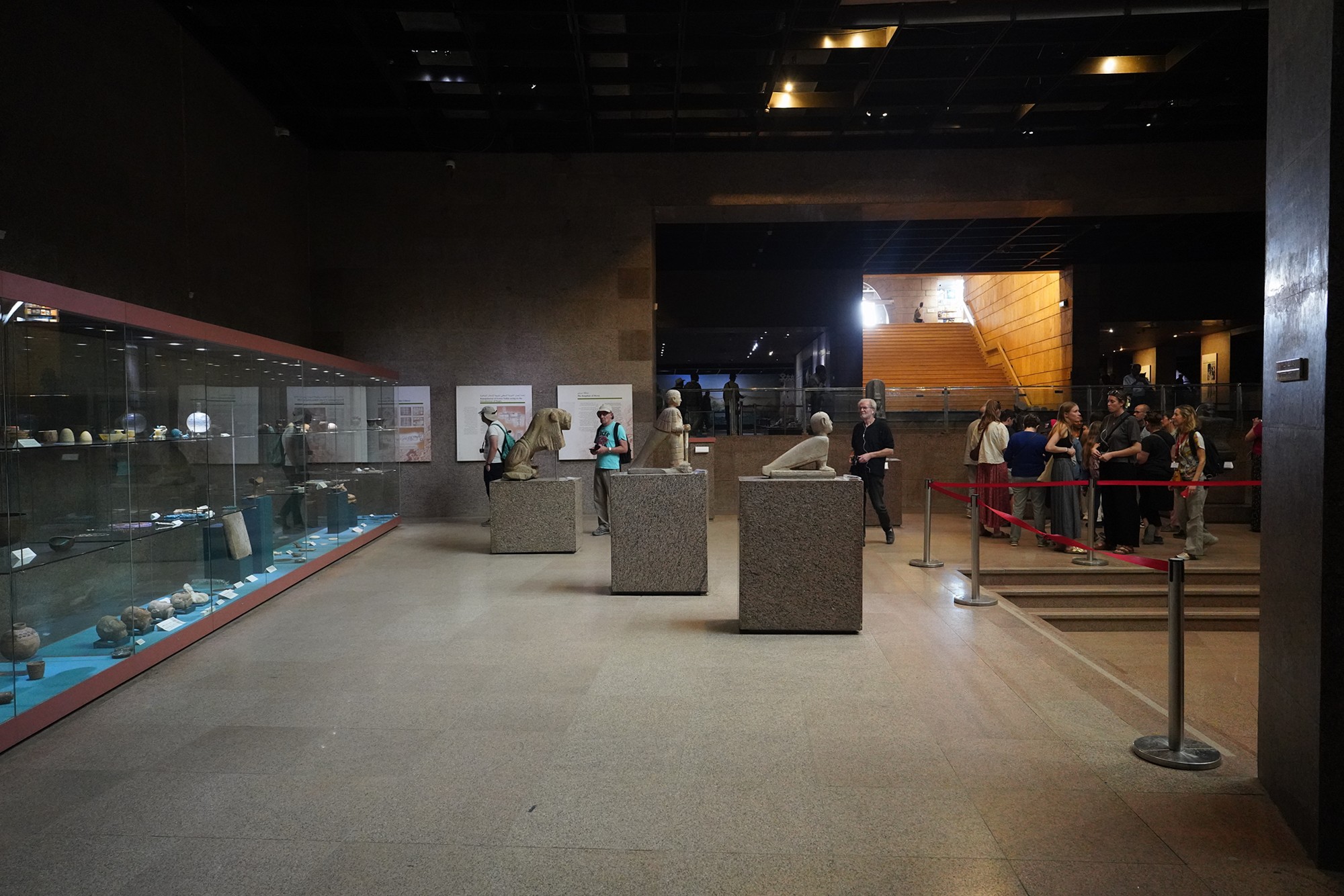
History museum always starts with the Stone Age.






Nubia has a rich history that predates the pharaonic civilization of ancient Egypt. The Nubians established powerful kingdoms and traded with neighboring regions. The interaction between Nubia and Egypt varied from cooperation to conflict over the centuries.
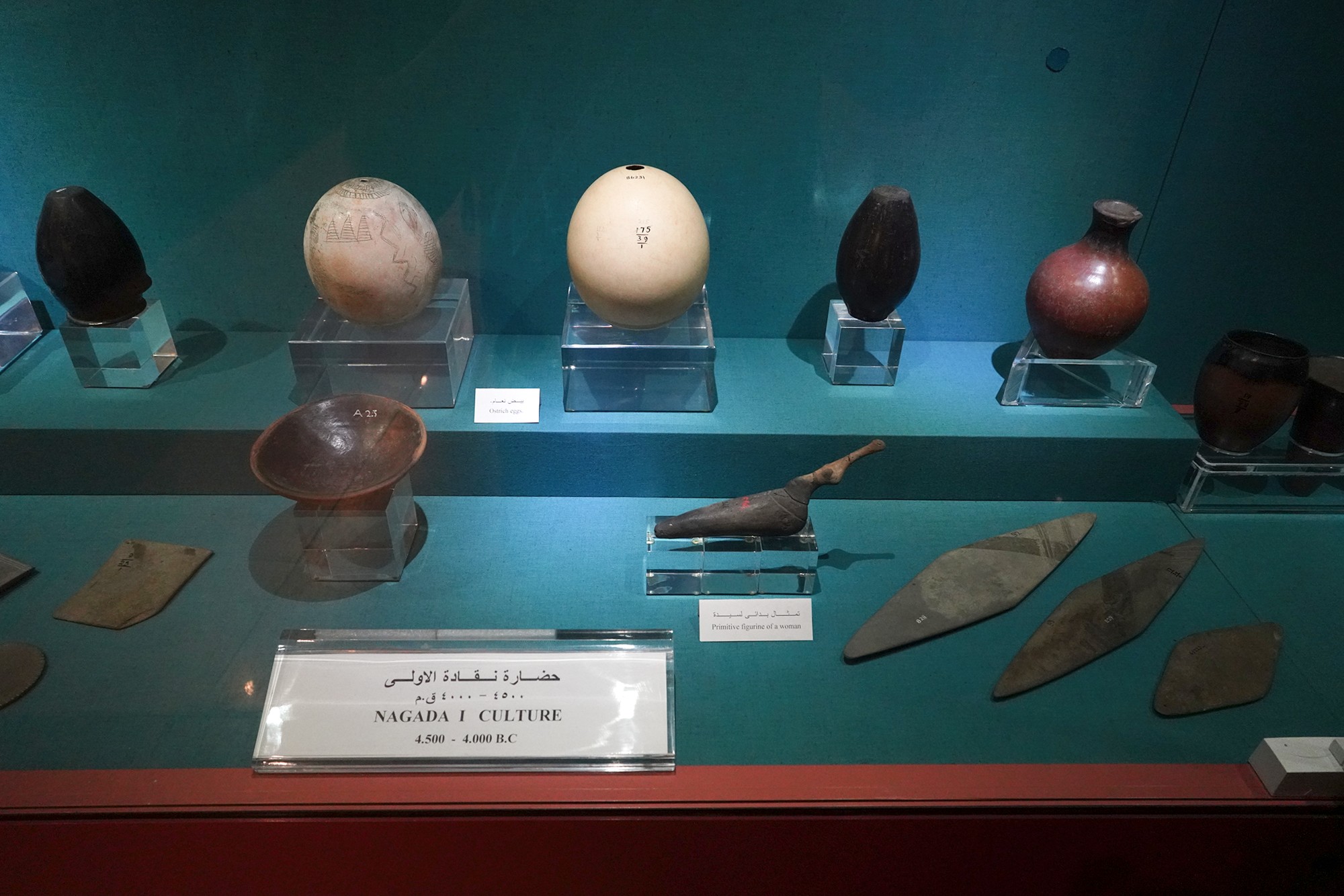
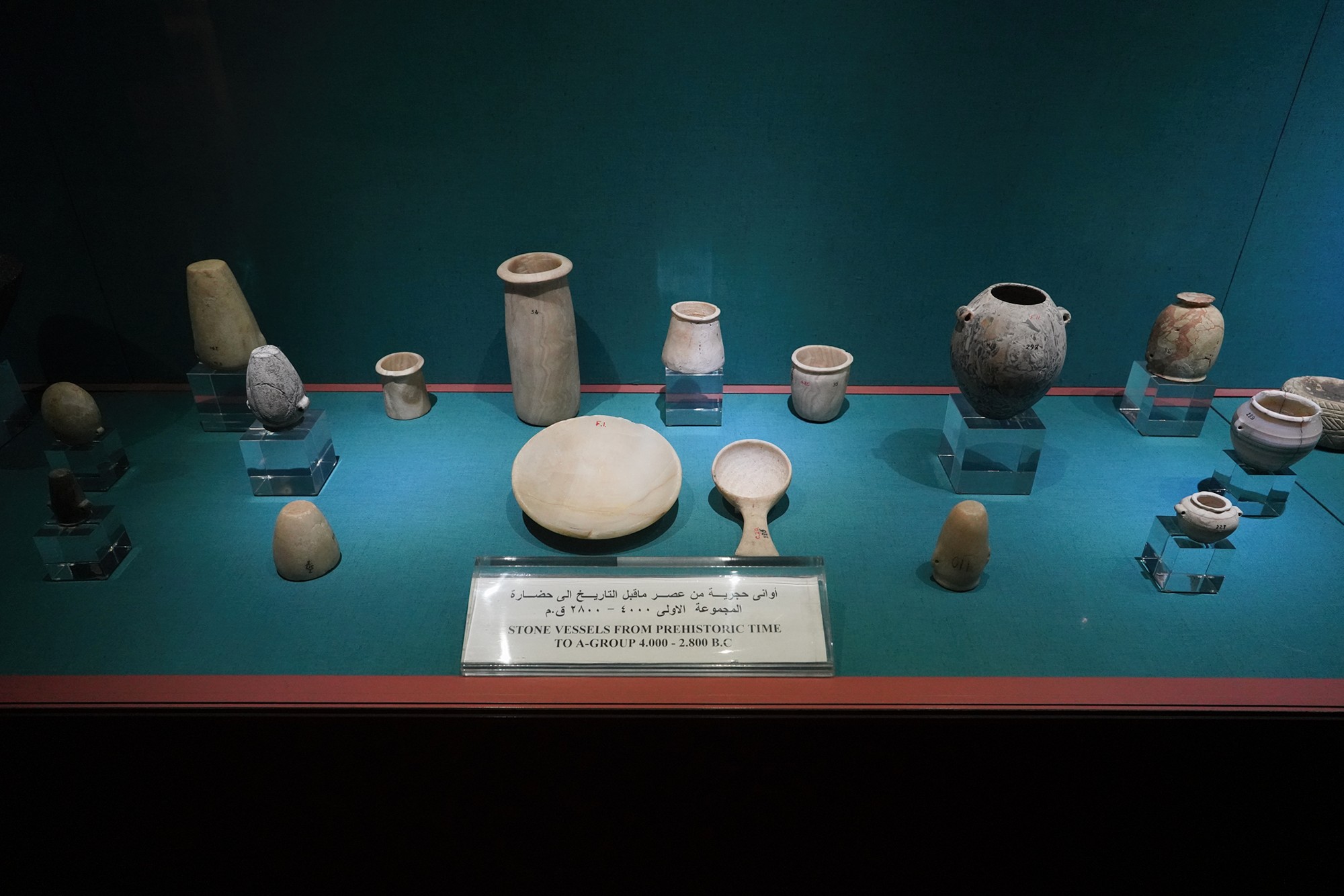
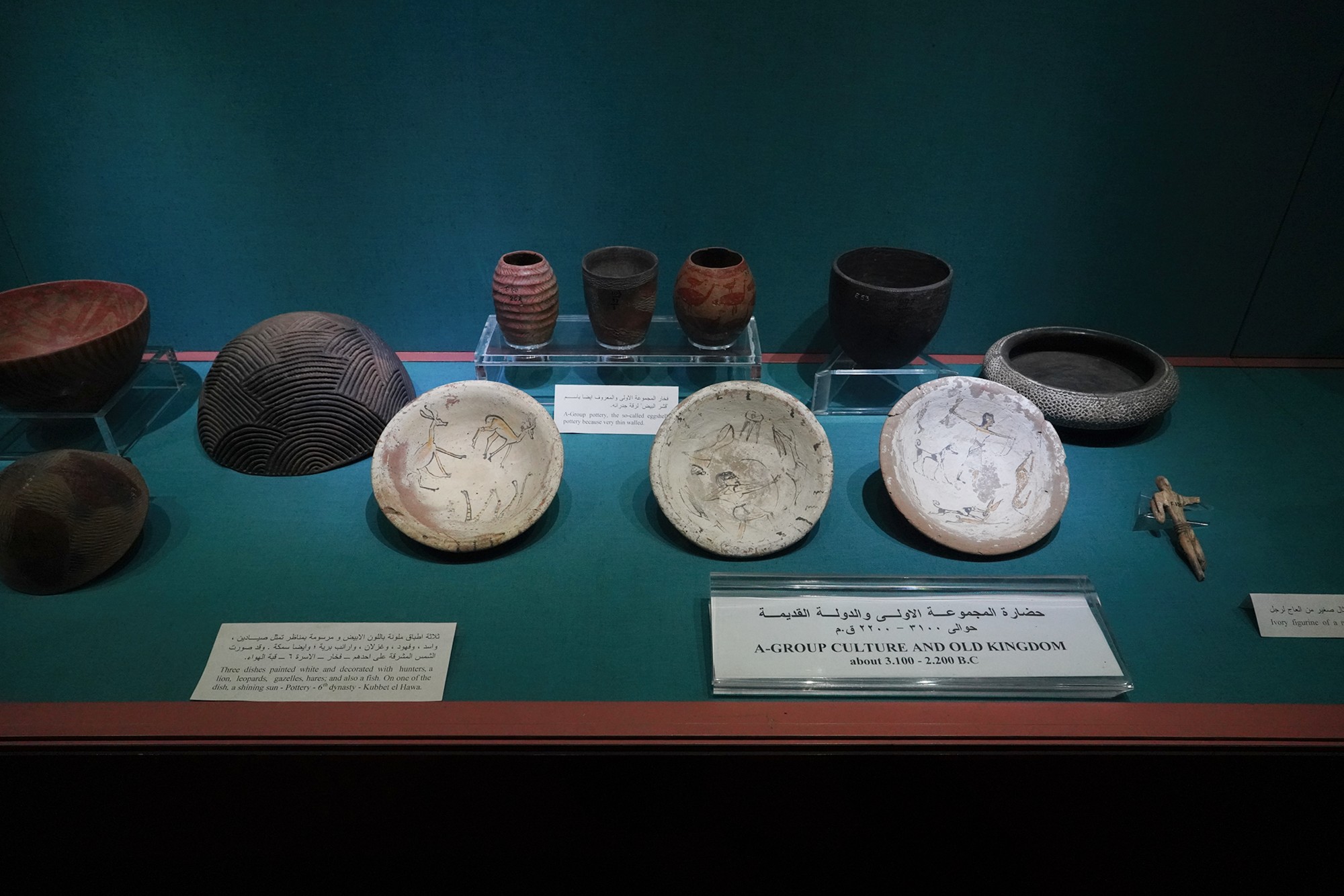








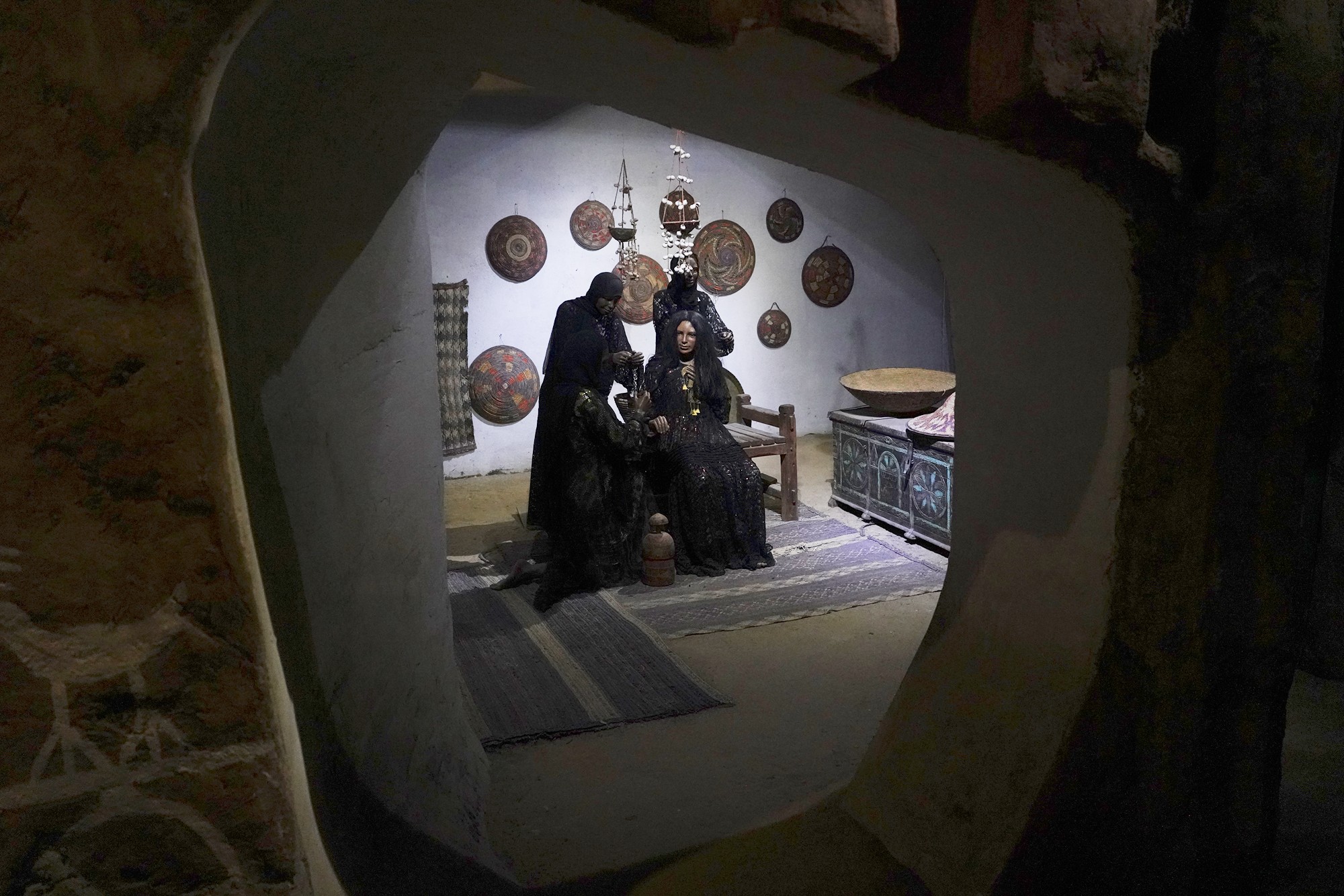
While Nubia shares some cultural elements with ancient Egypt, the Nubian people have maintained a distinctive cultural identity. This includes their language, traditions, architecture, and artistic expressions.
The Nubian A-Group is an archaeological term used to describe a prehistoric culture that existed in Nubia (northern Sudan and southern Egypt) during the late Neolithic and early Bronze Age periods. This culture is named after the alphabetical system used by archaeologists to categorize various archaeological sites in Nubia. The A-Group culture predates the more well-known ancient Egyptian civilization and played a significant role in the region’s prehistory.








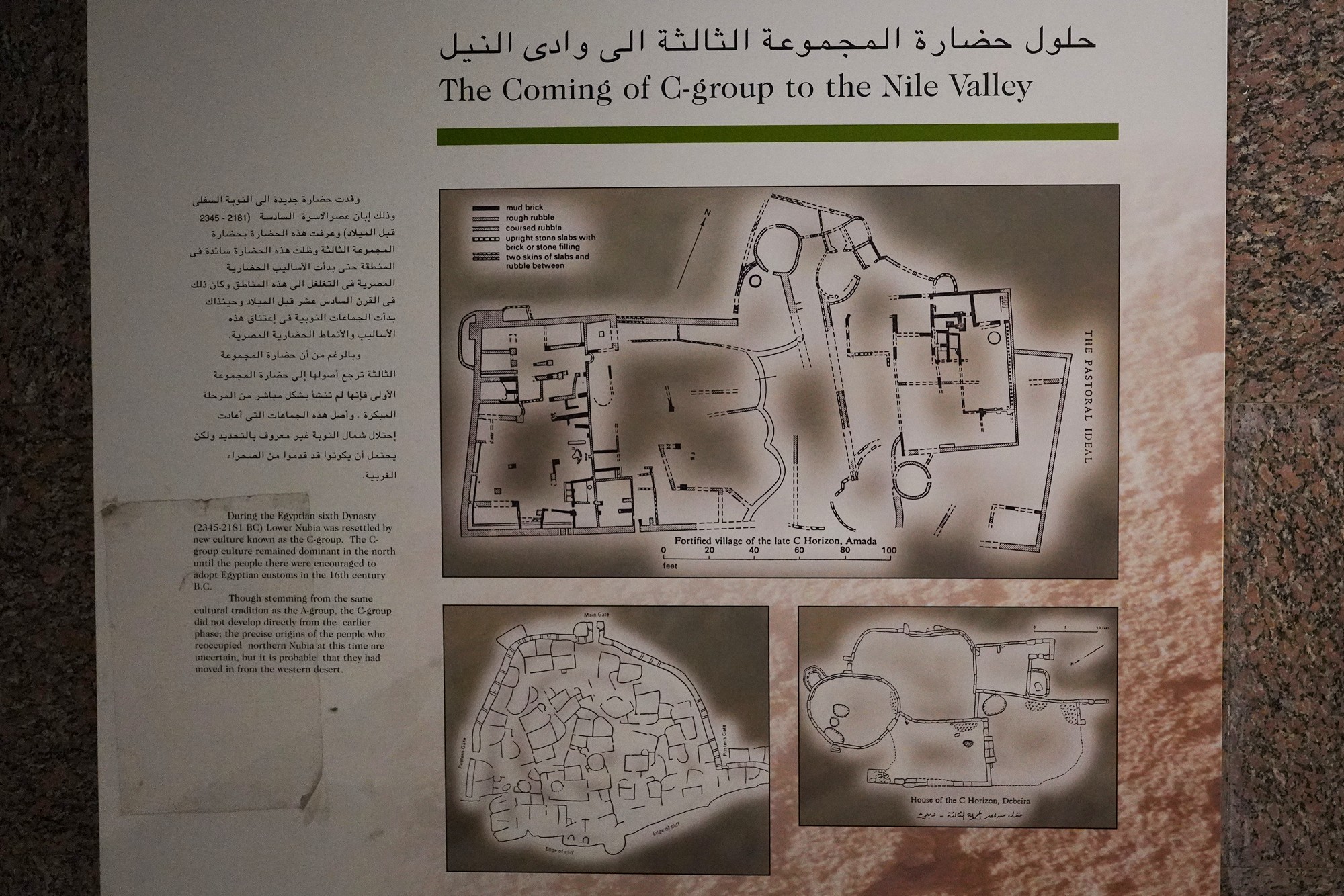
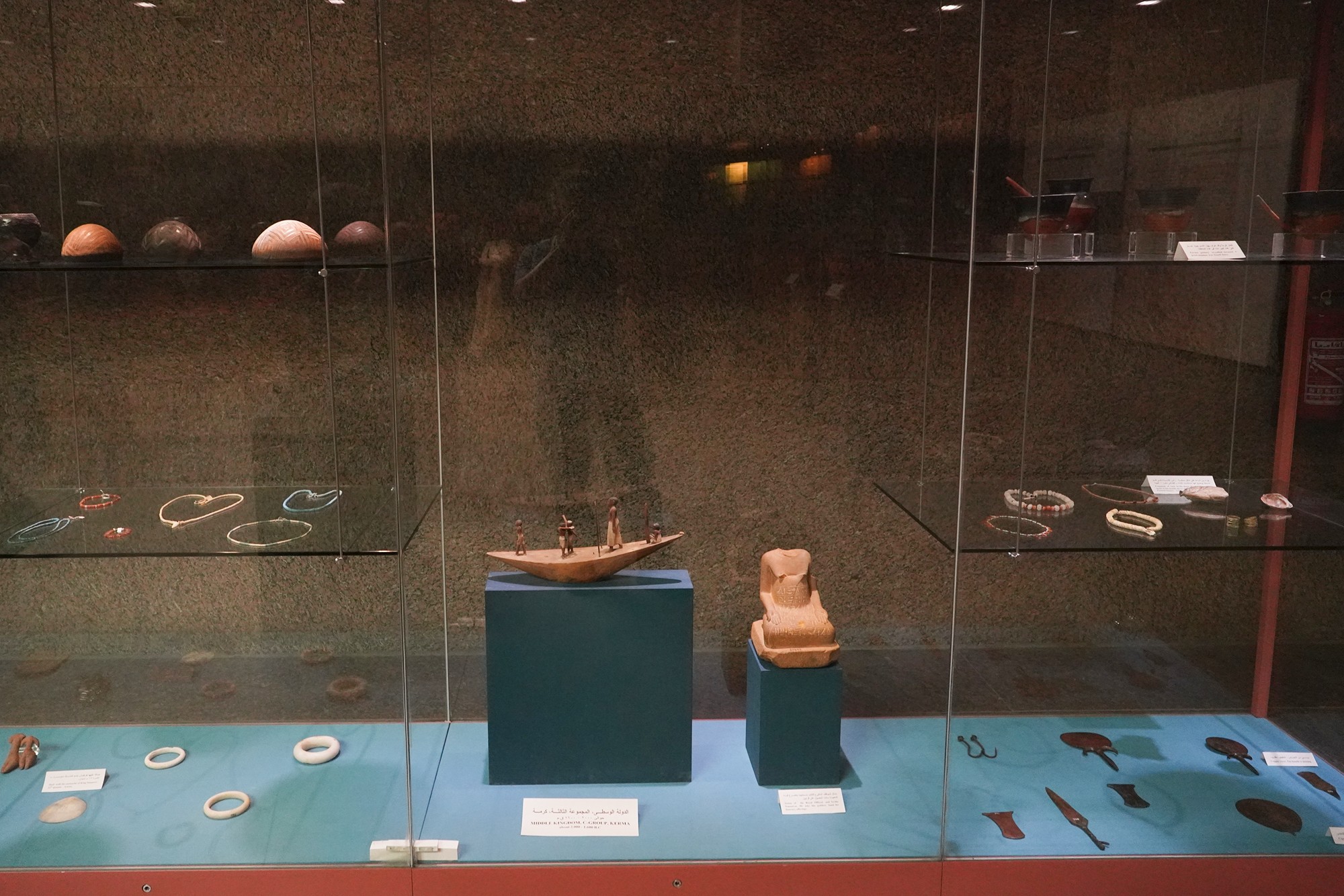
The Nubian C-Group refers to a cultural and archaeological phase that followed the Nubian A-Group in the Nile Valley. The C-Group culture emerged around 2300 BCE and persisted until approximately 1550 BCE. This period falls within the later part of the Bronze Age in Nubia, and it represents a stage of cultural development and interaction between Nubia and Egypt.
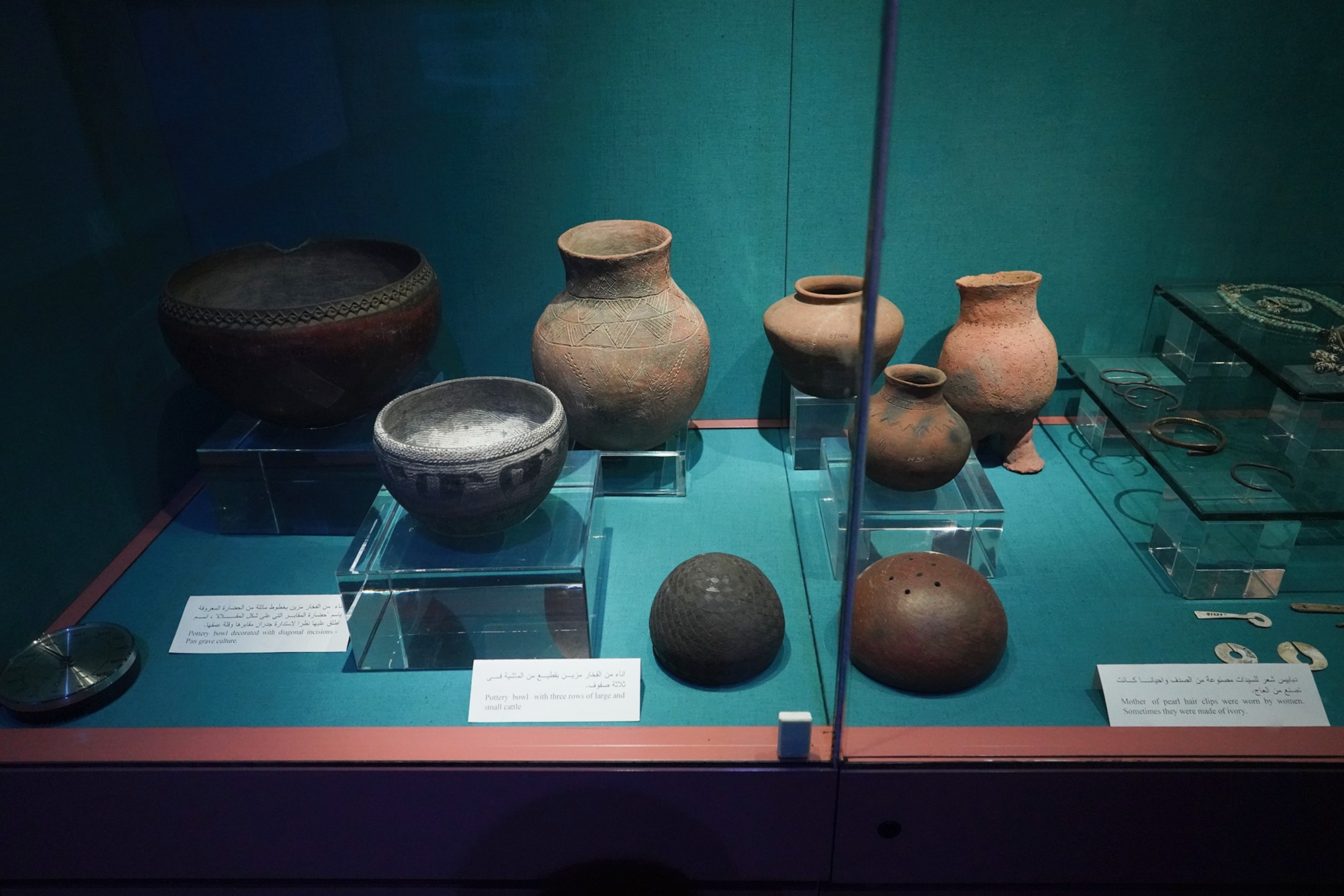
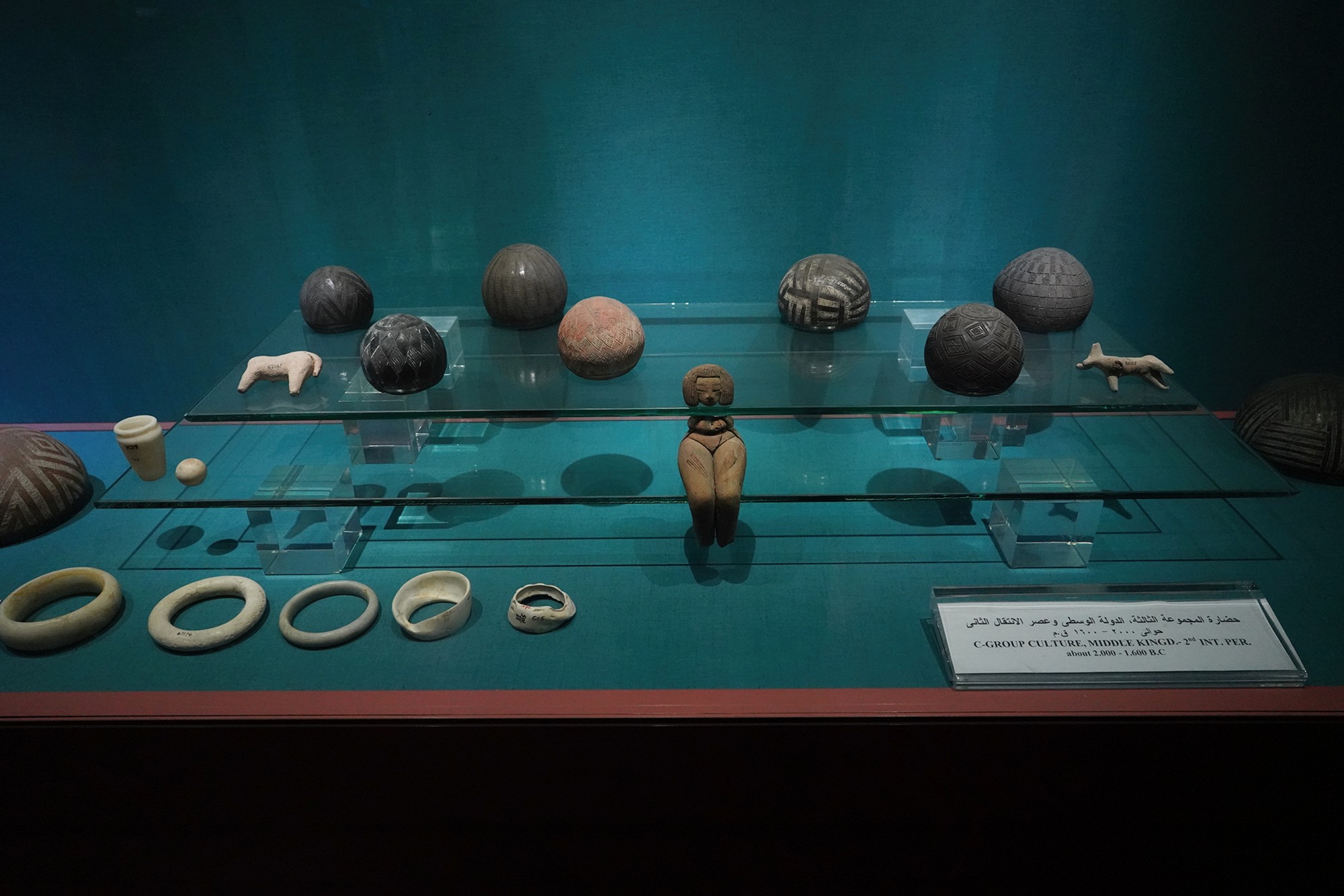
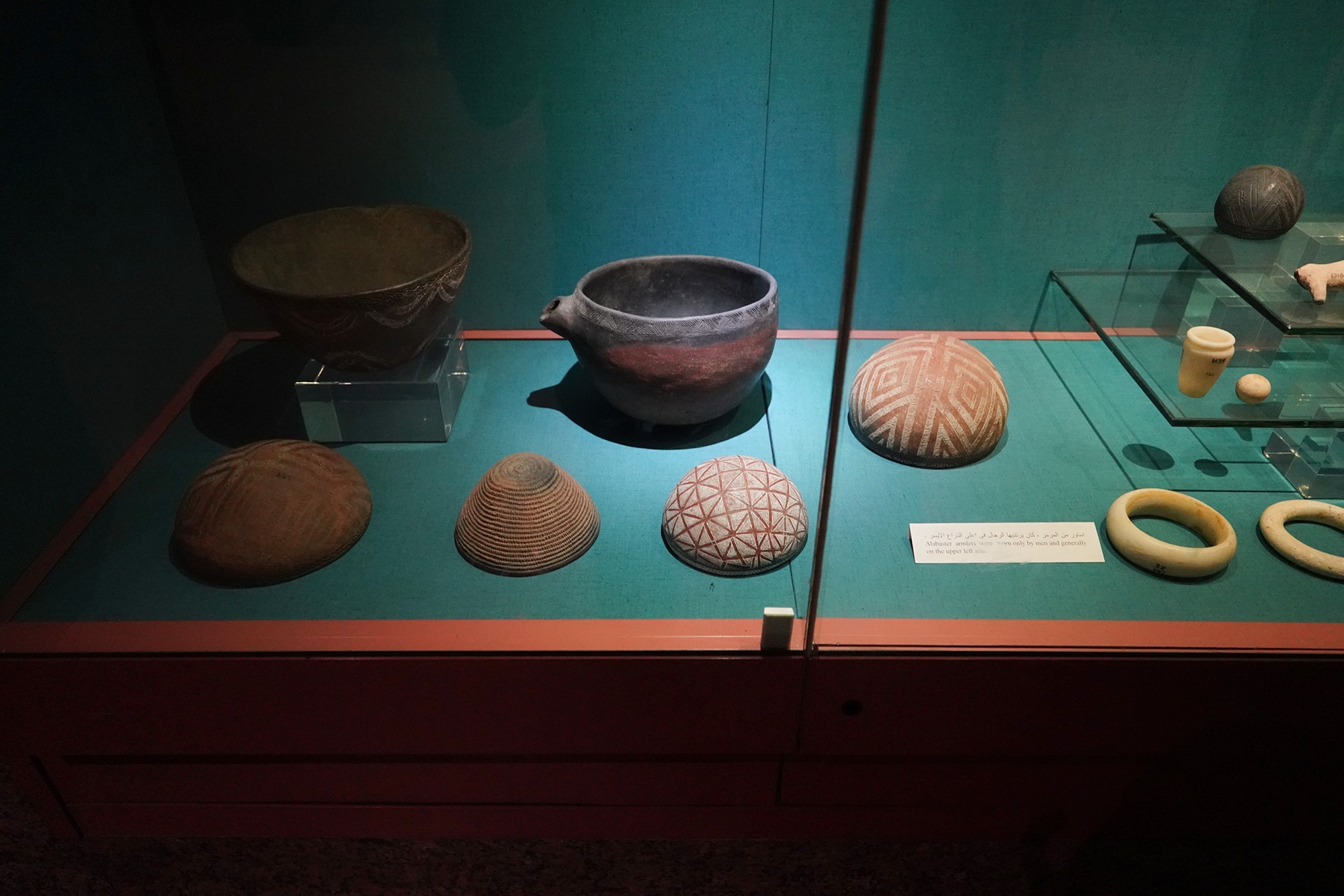
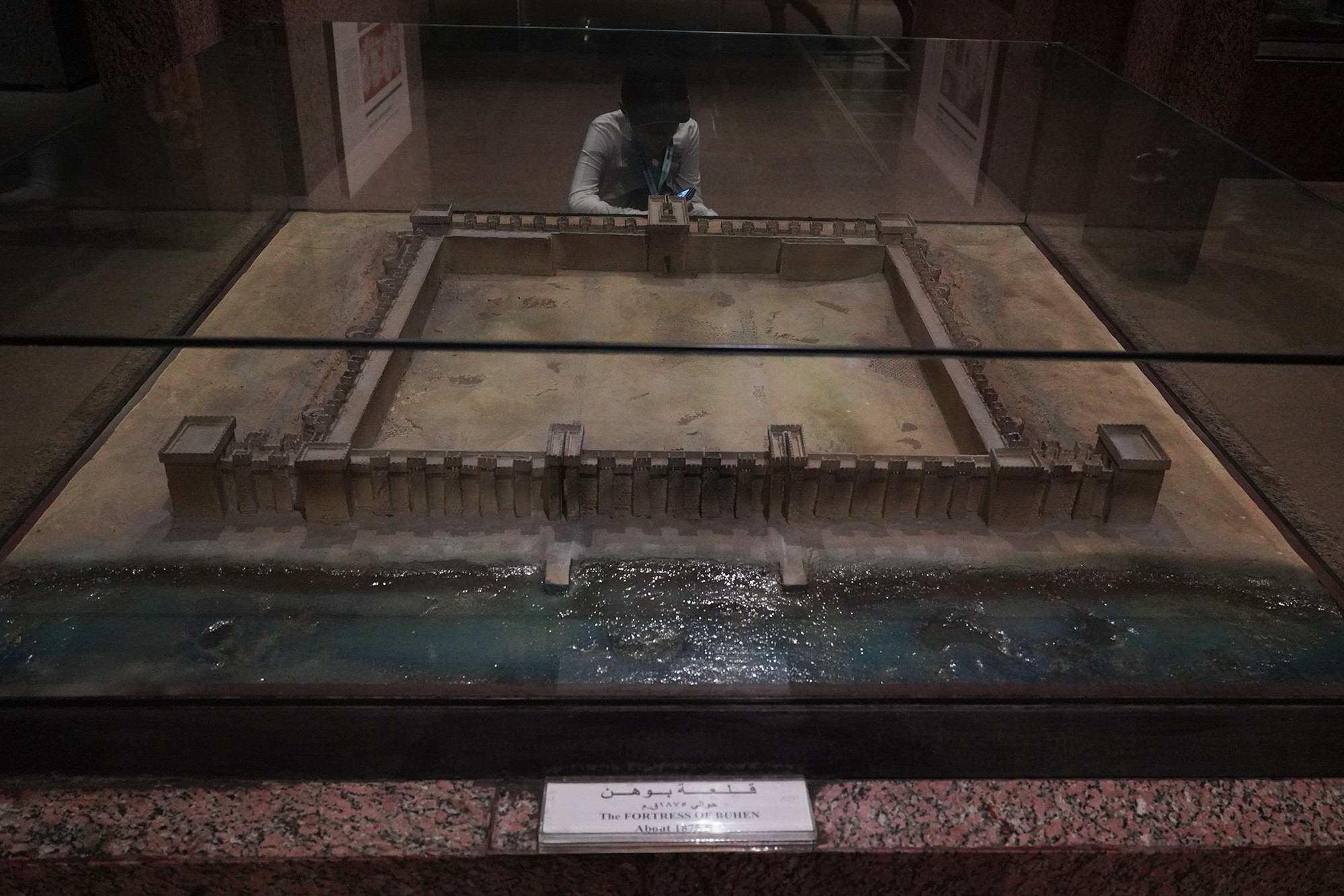

















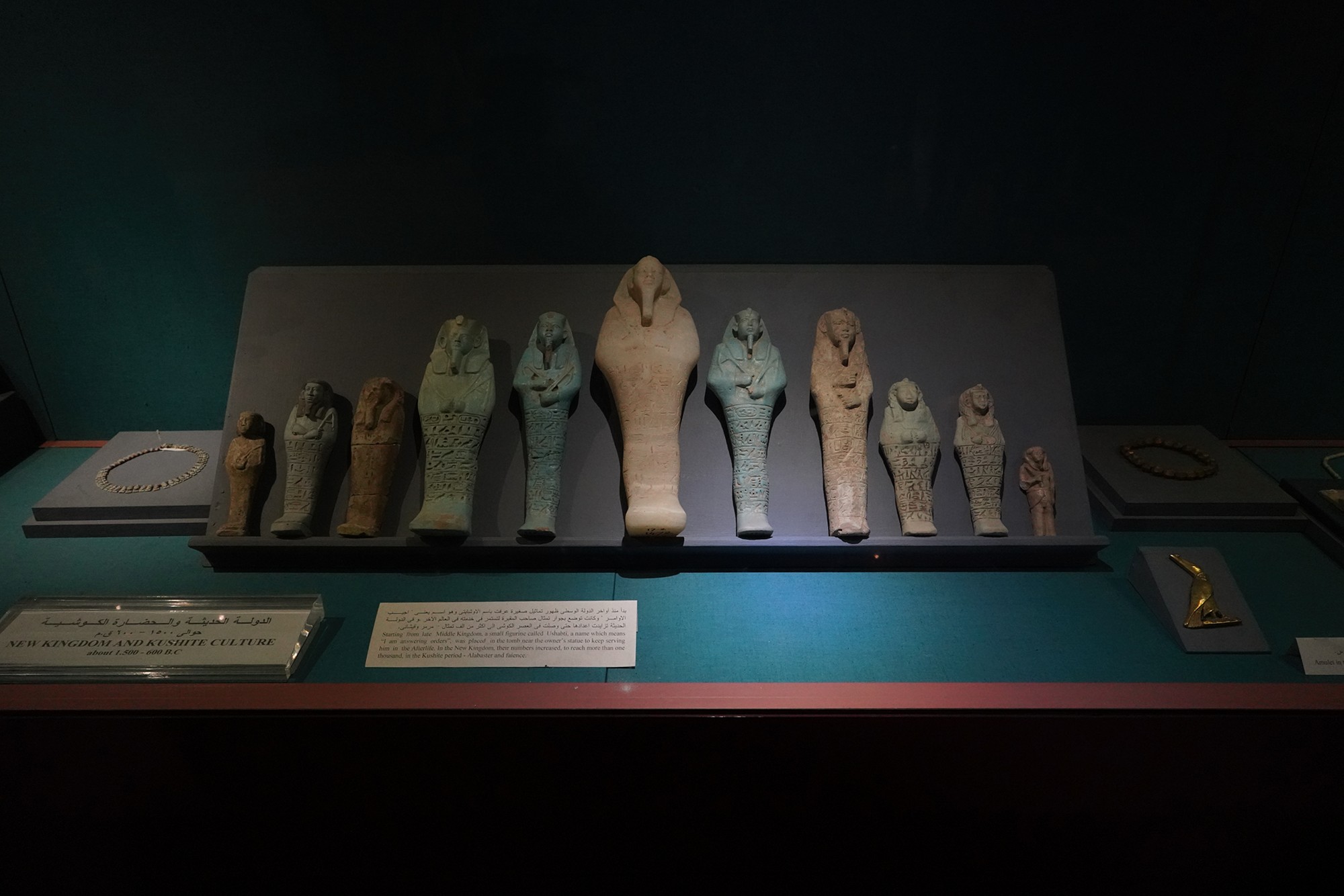
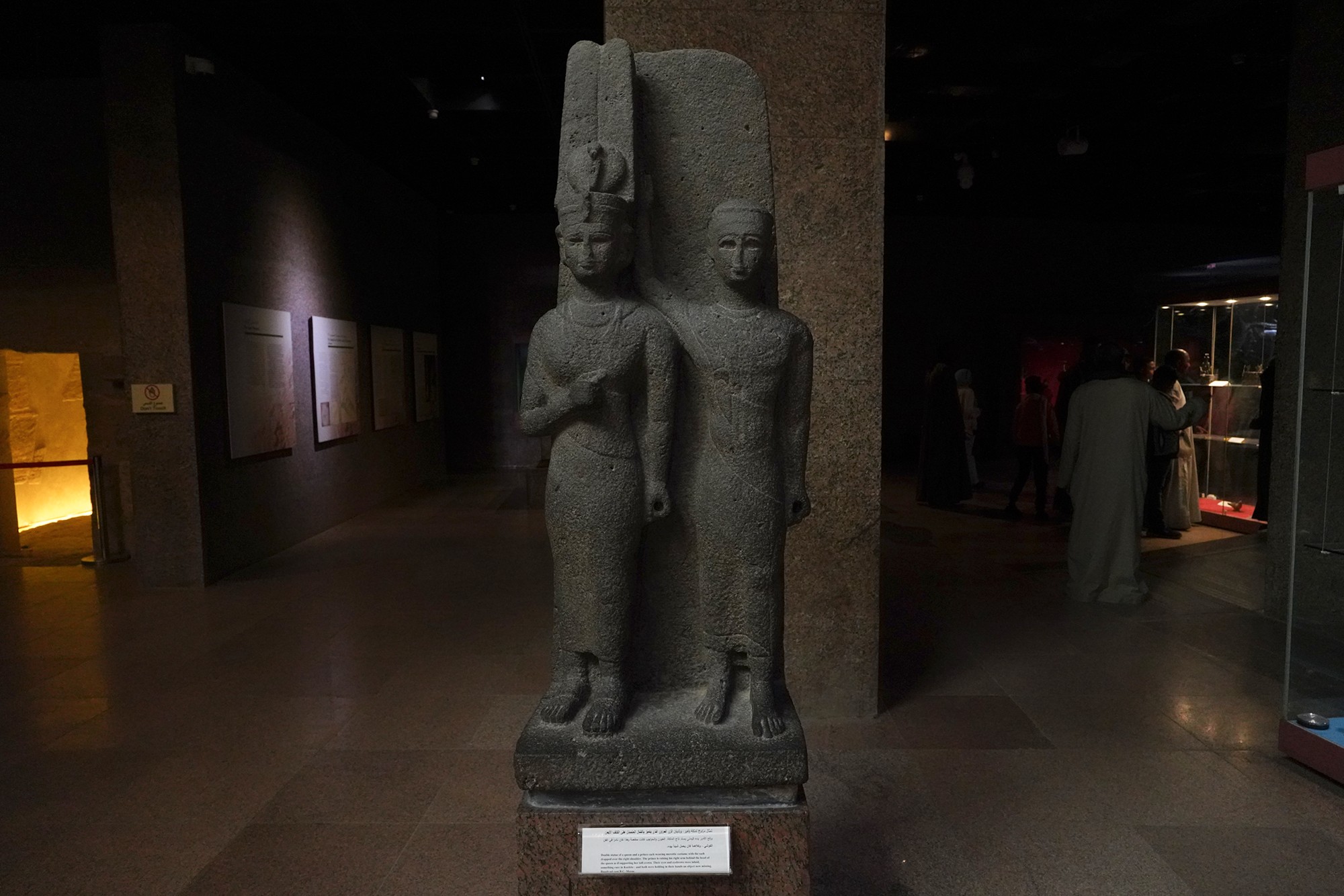
The Kushite Dynasty, also known as the 25th Dynasty, refers to a period in ancient Egyptian history when rulers from the Kingdom of Kush, located in Nubia (present-day Sudan), conquered and ruled over Egypt. This dynasty is significant for being a foreign dynasty that came to power in Egypt, marking a period of cultural interaction and influence between the Nubian and Egyptian civilizations.
The Kushite Dynasty came to power after King Piye, also known as Piankhi, successfully conquered Egypt around 747 BCE. Piye’s conquest marked the end of the 24th Dynasty and the beginning of the 25th Dynasty.

The Kushite Dynasty faced challenges from the Assyrians, who invaded Egypt in the 7th century BCE. The Assyrians successfully drove the Kushite rulers out of Egypt, marking the end of the 25th Dynasty. The Kushite rulers returned to Nubia, where they continued to rule over the Kingdom of Kush.











The Kingdom of Meroë is often considered the successor to the Kingdom of Kush, which had its capital at Napata. The shift in the capital to Meroë marked a new phase in Nubian history.
Meroë was strategically located for trade between the Mediterranean and sub-Saharan Africa. The kingdom engaged in trade with Egypt, the Roman Empire, and other African regions. It was a center for iron production, and the Meroitic iron industry was highly developed.
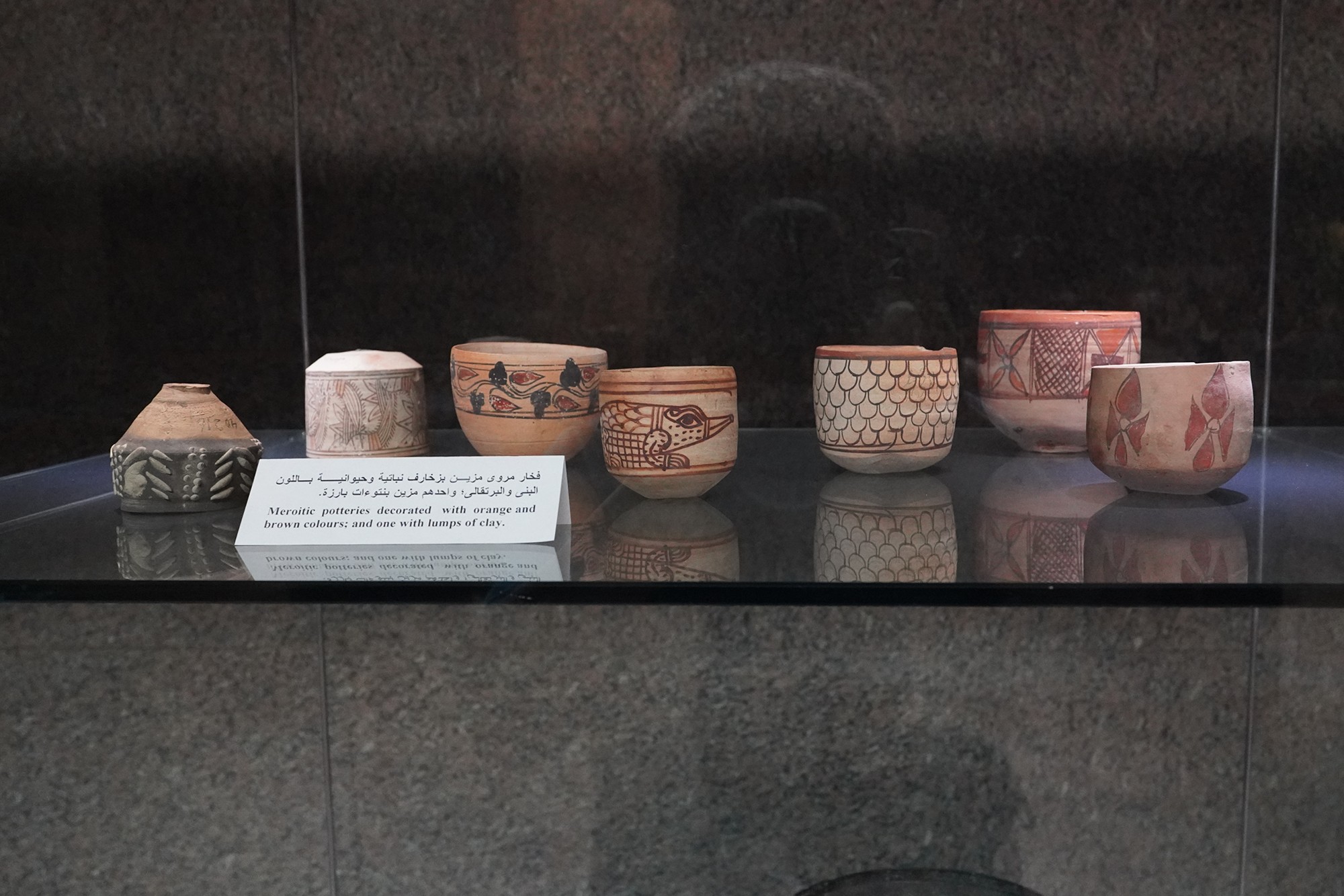








The reasons for the decline of Meroë are not fully understood, but factors such as environmental changes, shifts in trade routes, and possible conflicts with neighboring cultures may have played a role. The city of Meroë and its surrounding areas were eventually abandoned.







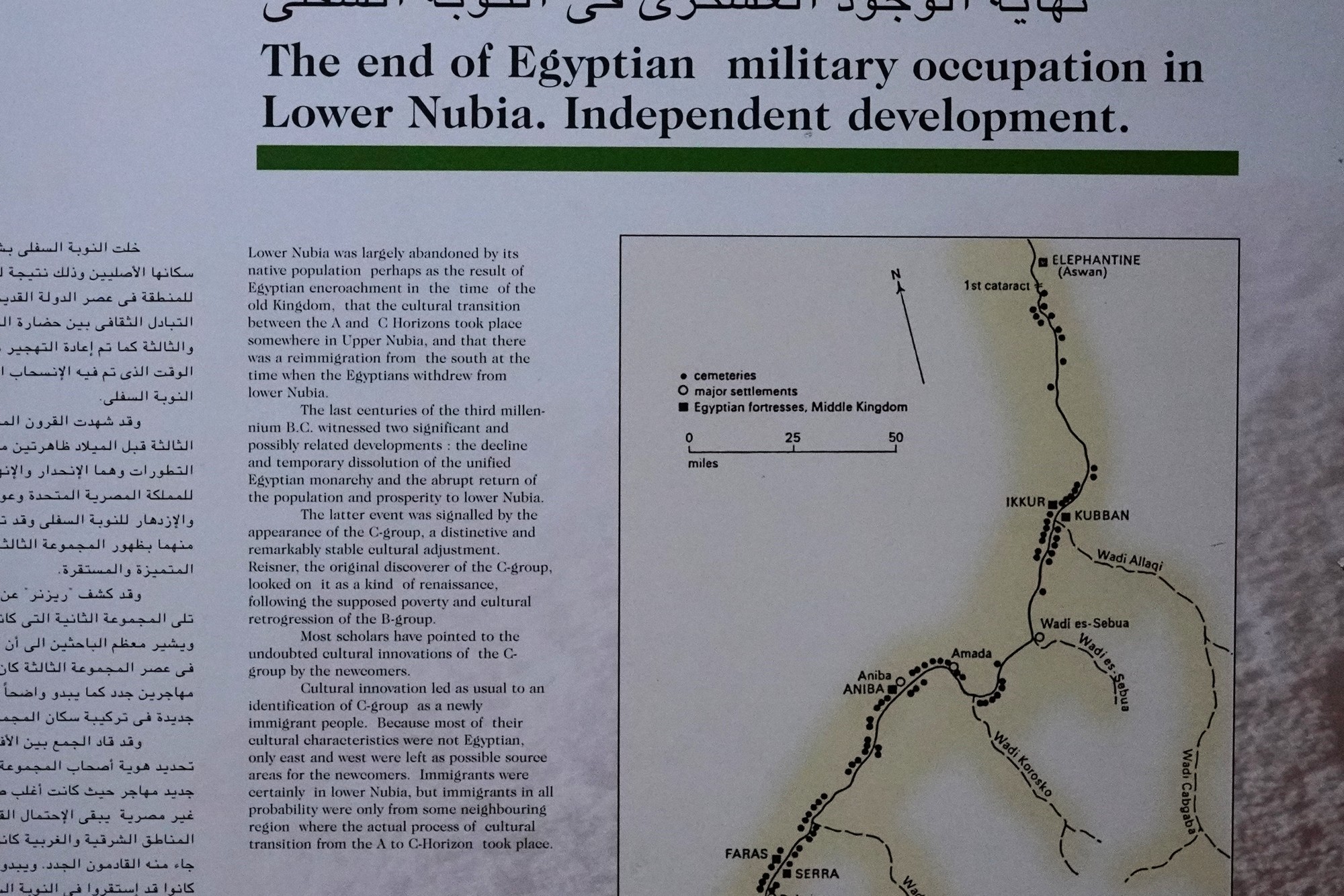
During the later centuries of the first millennium CE, the spread of Christianity reached Nubia. The Nubian kingdom of Nobatia, which emerged in the region of Lower Nubia (north of the Third Cataract), became one of the earliest Nubian kingdoms to adopt Christianity.
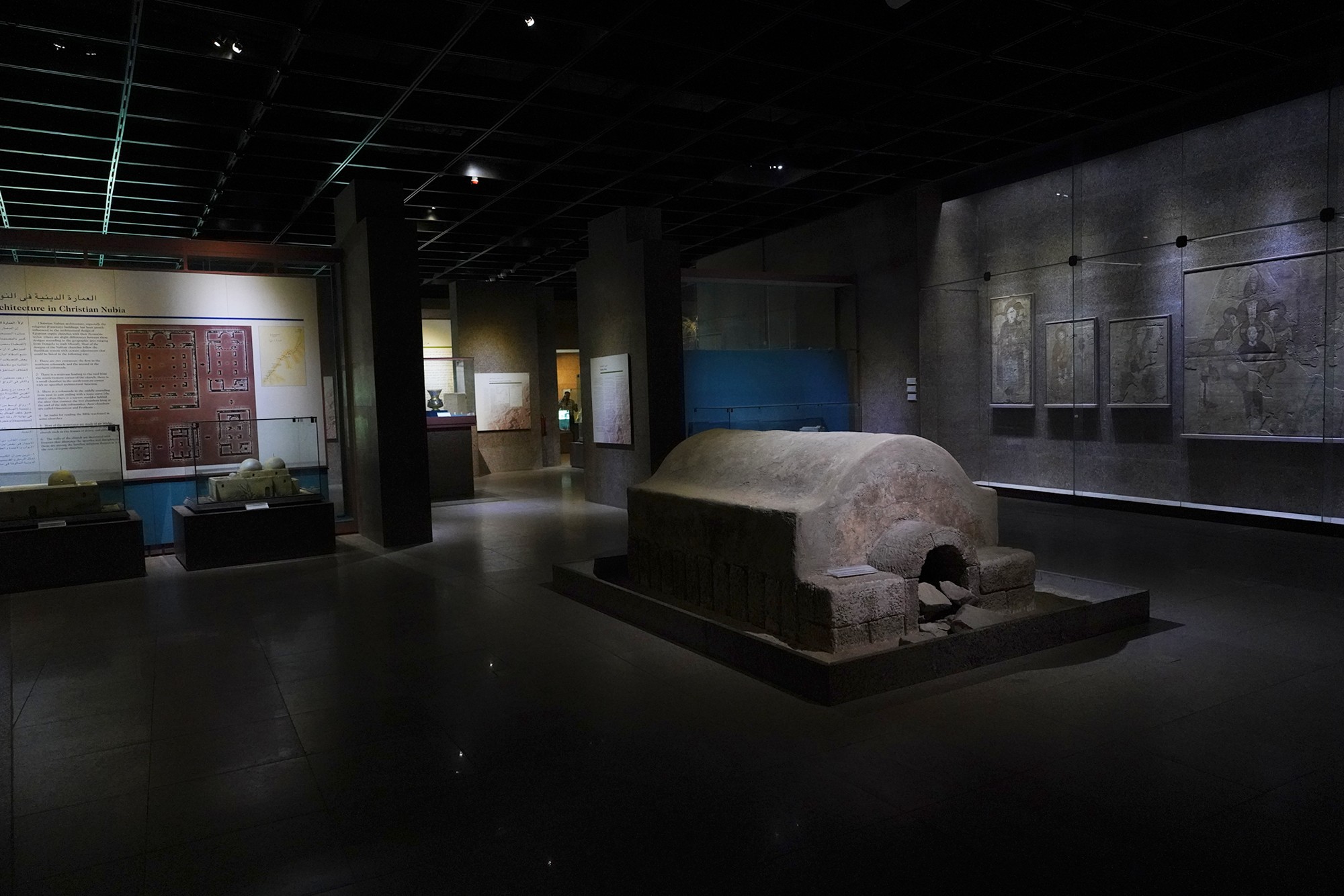
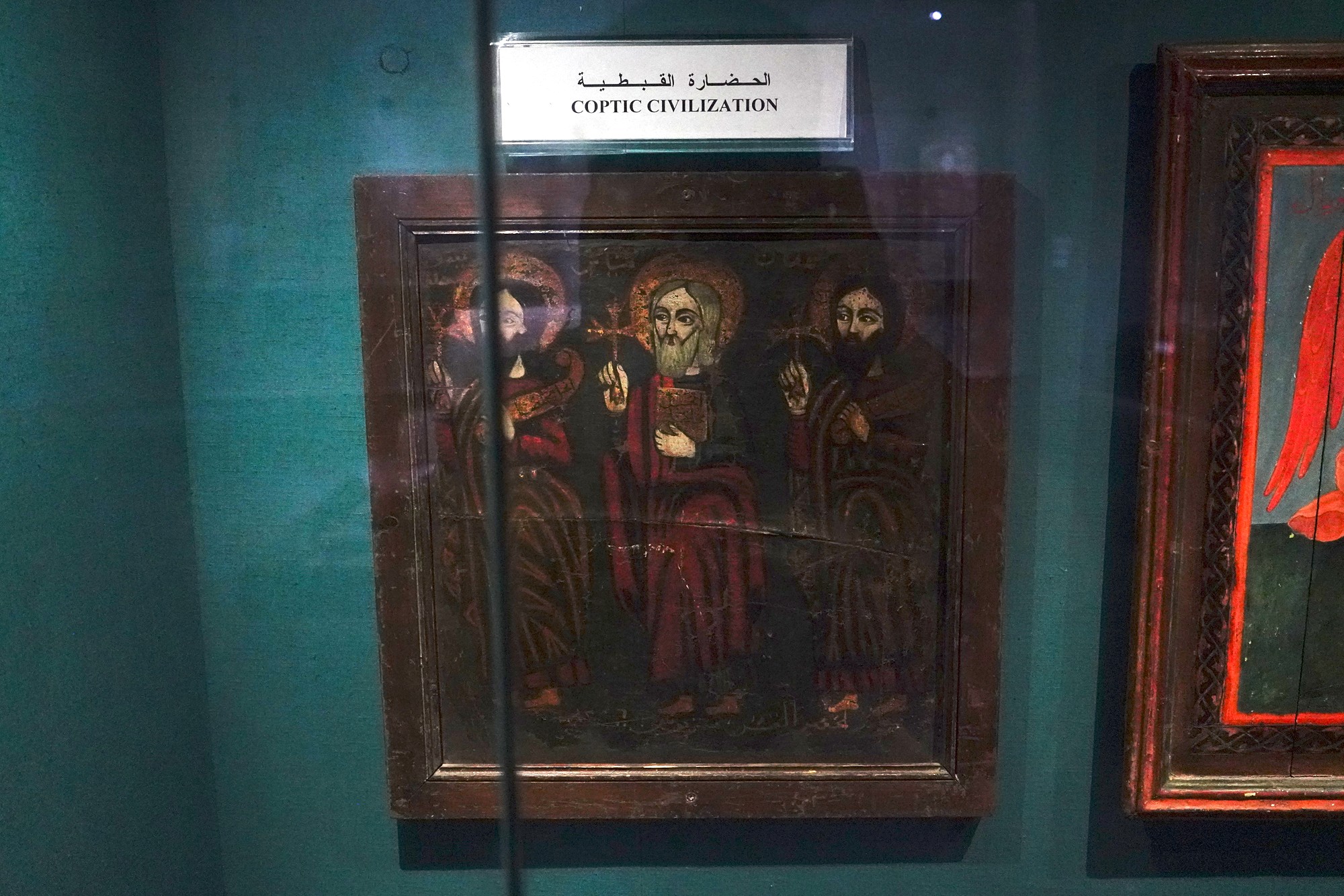
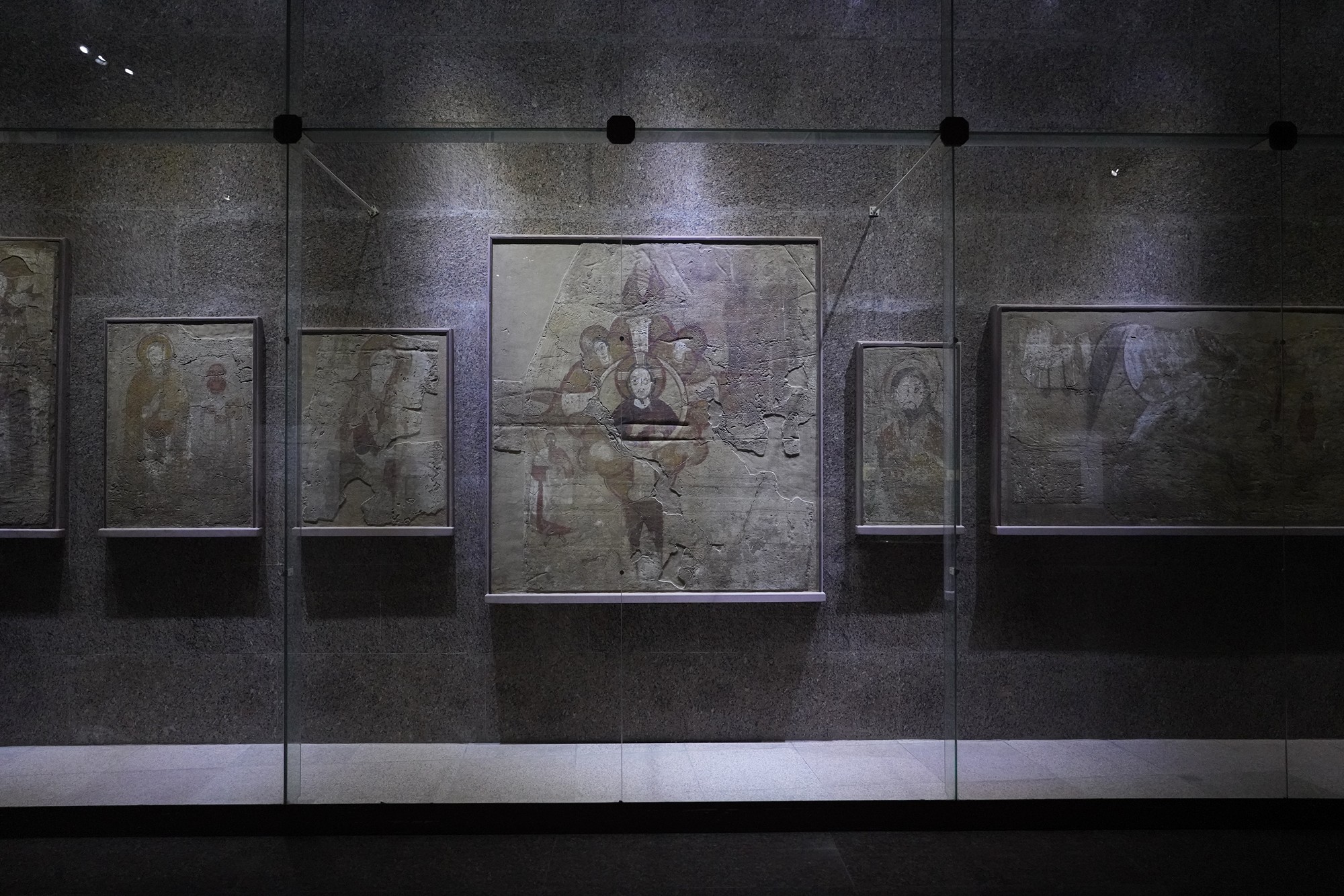












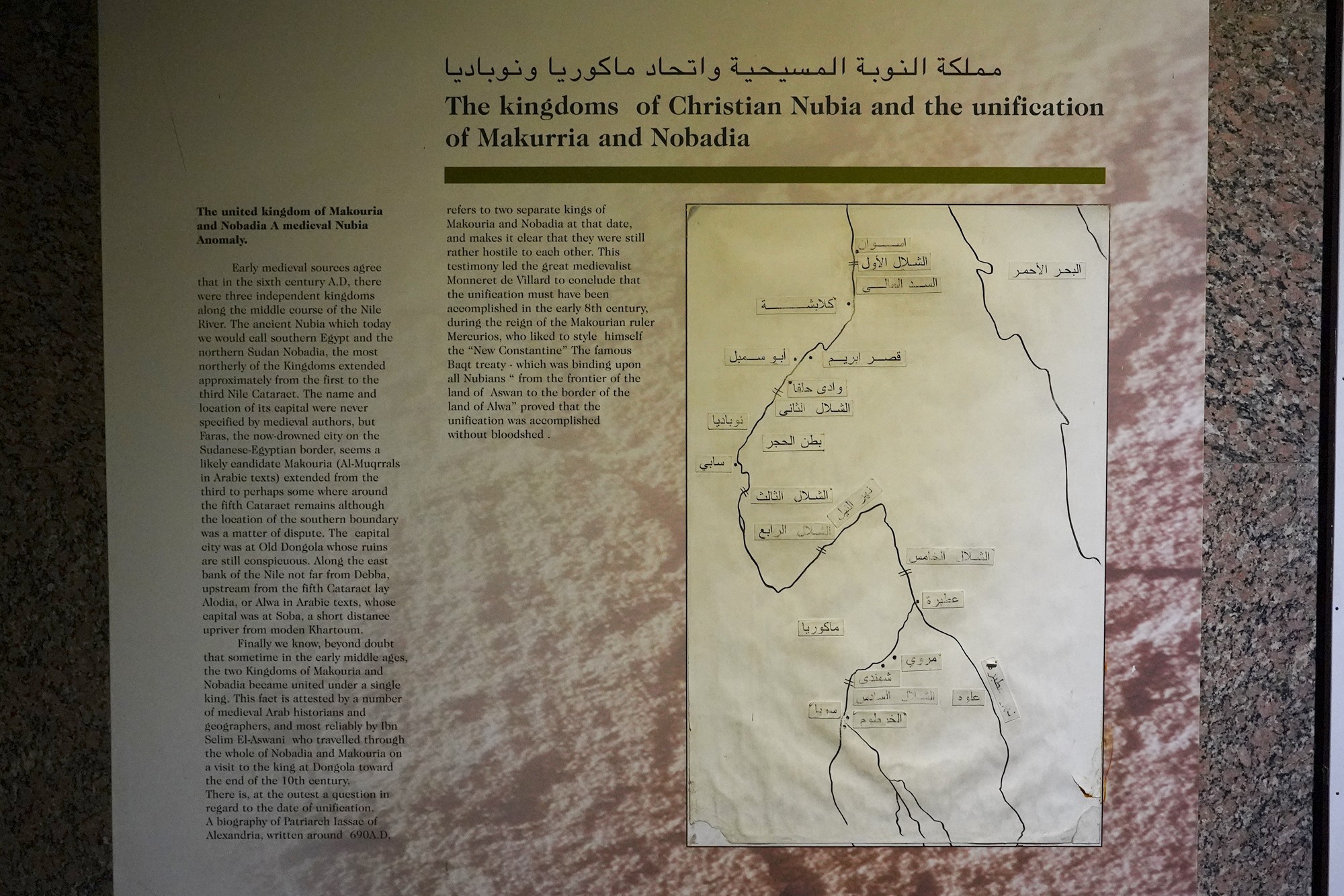



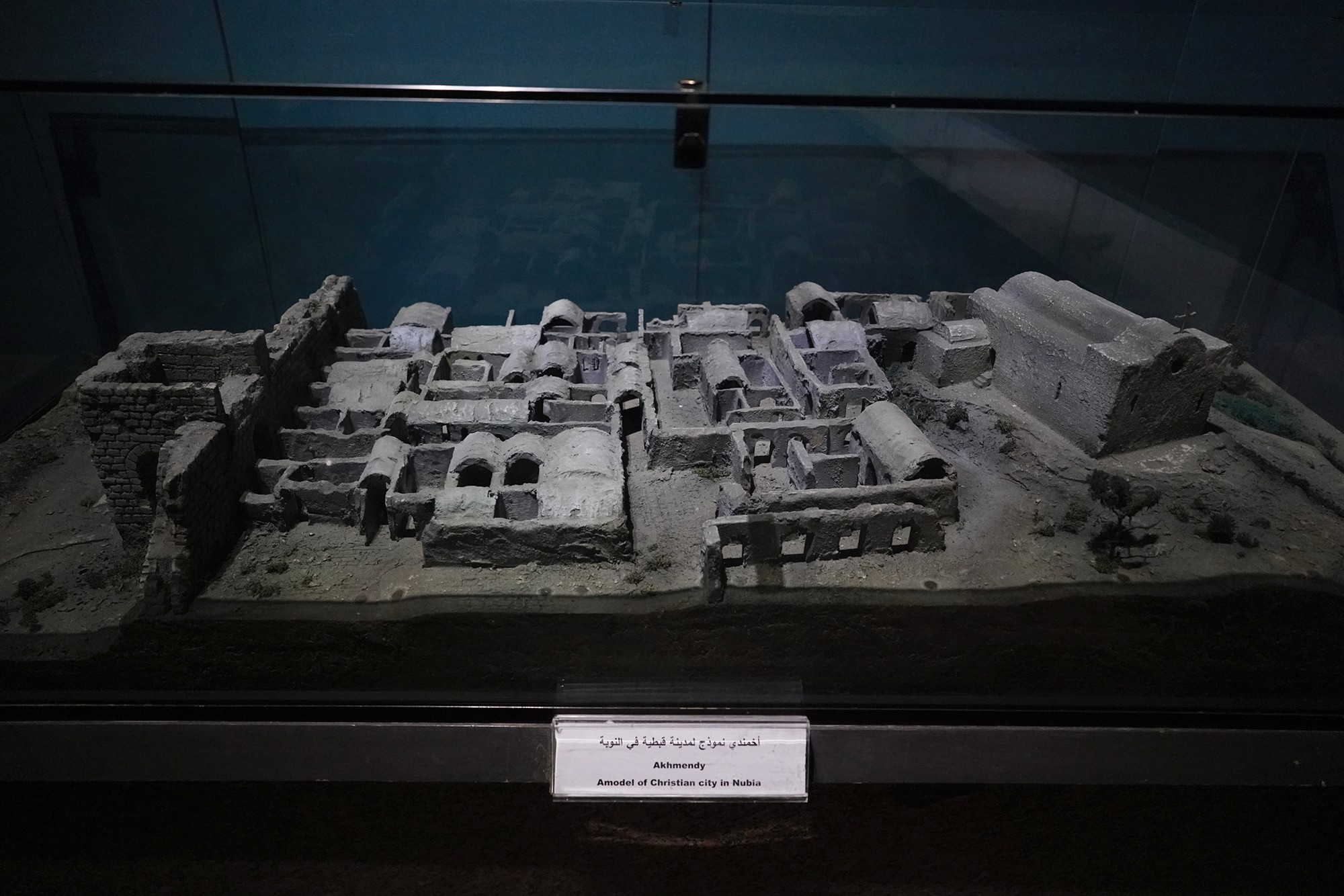

Over time, the Nubian kingdoms faced various challenges, including Islamic influences from the north. The decline of Makuria and Alodia occurred by the 14th century, and the region eventually came under the influence of Islamic states.
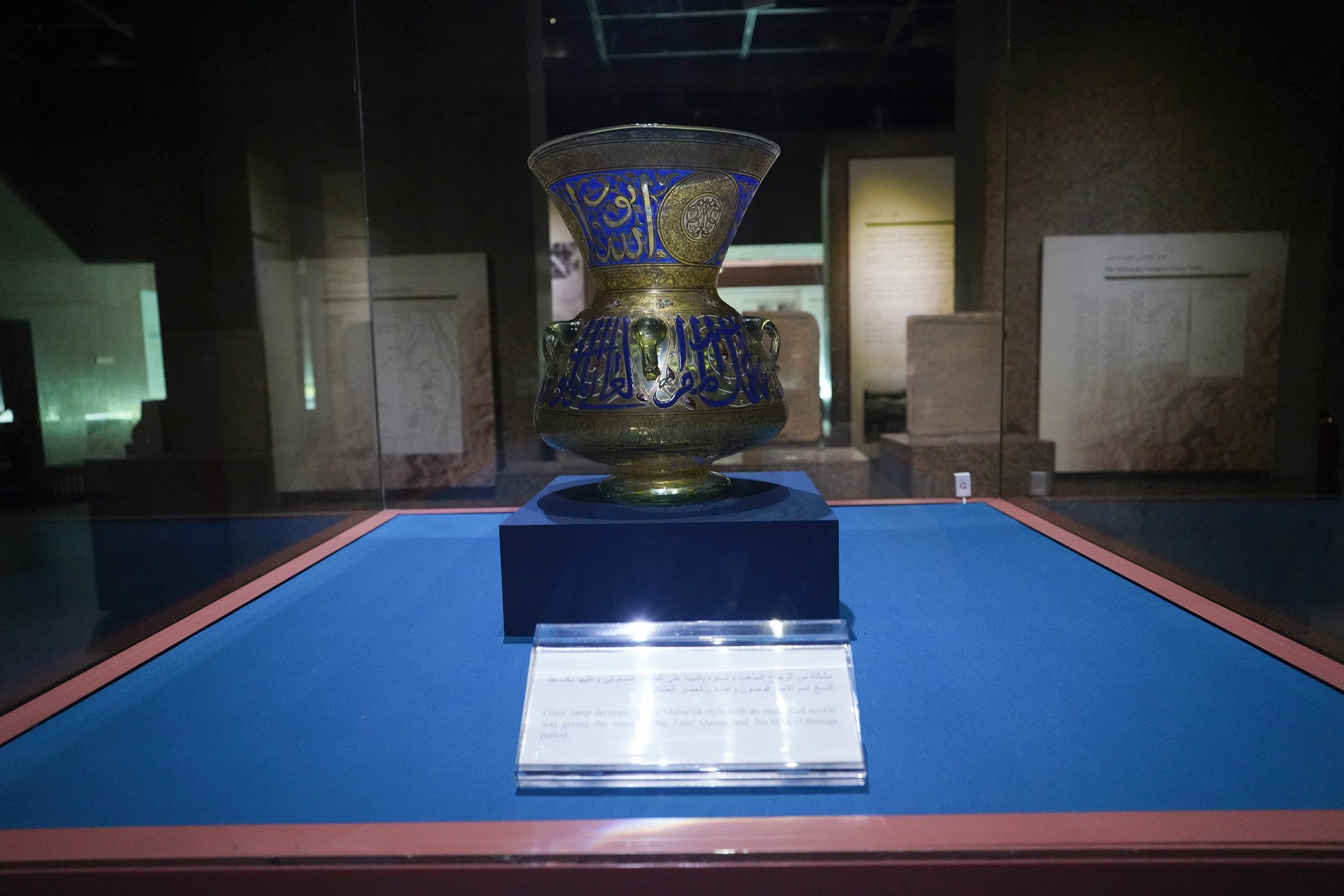
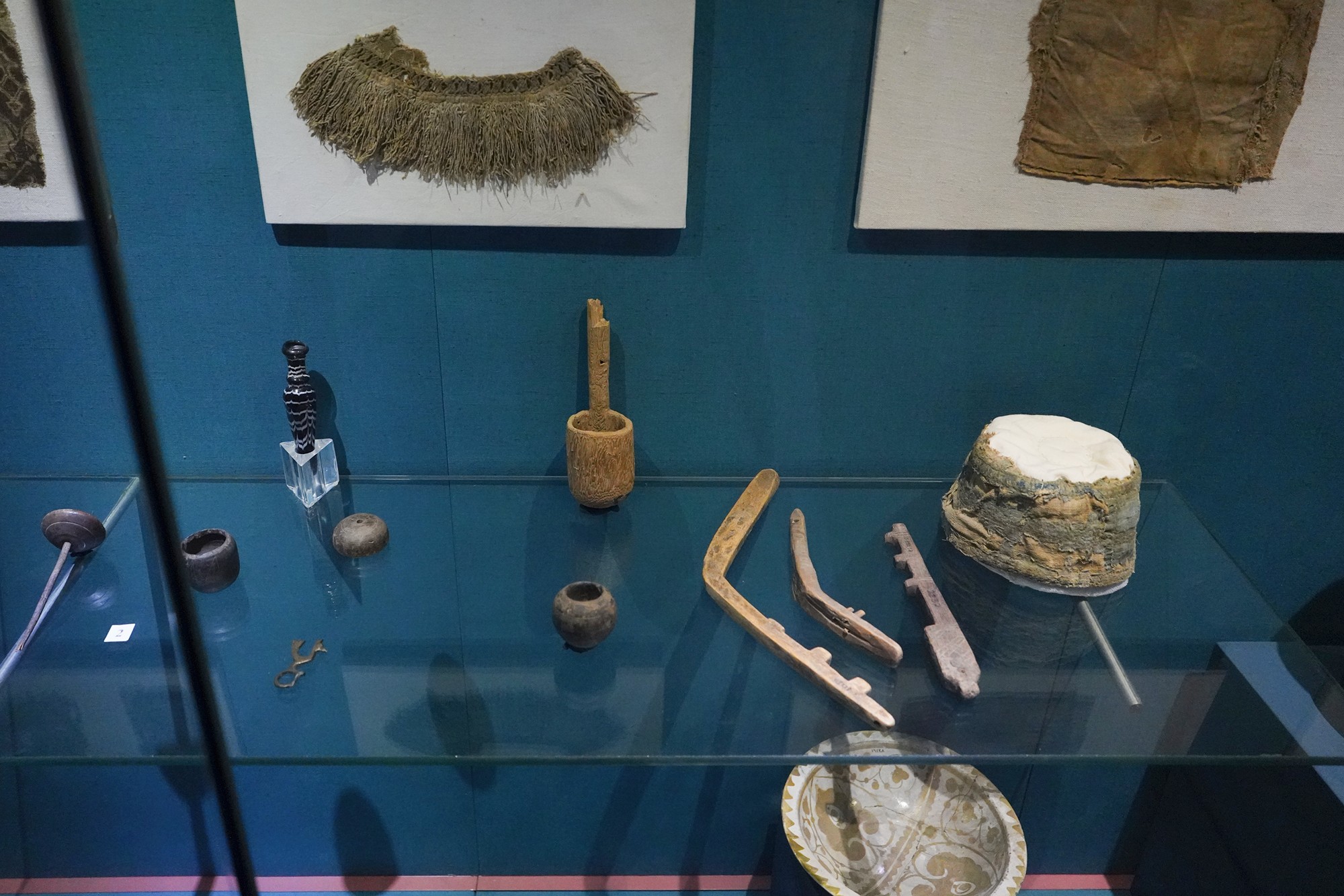
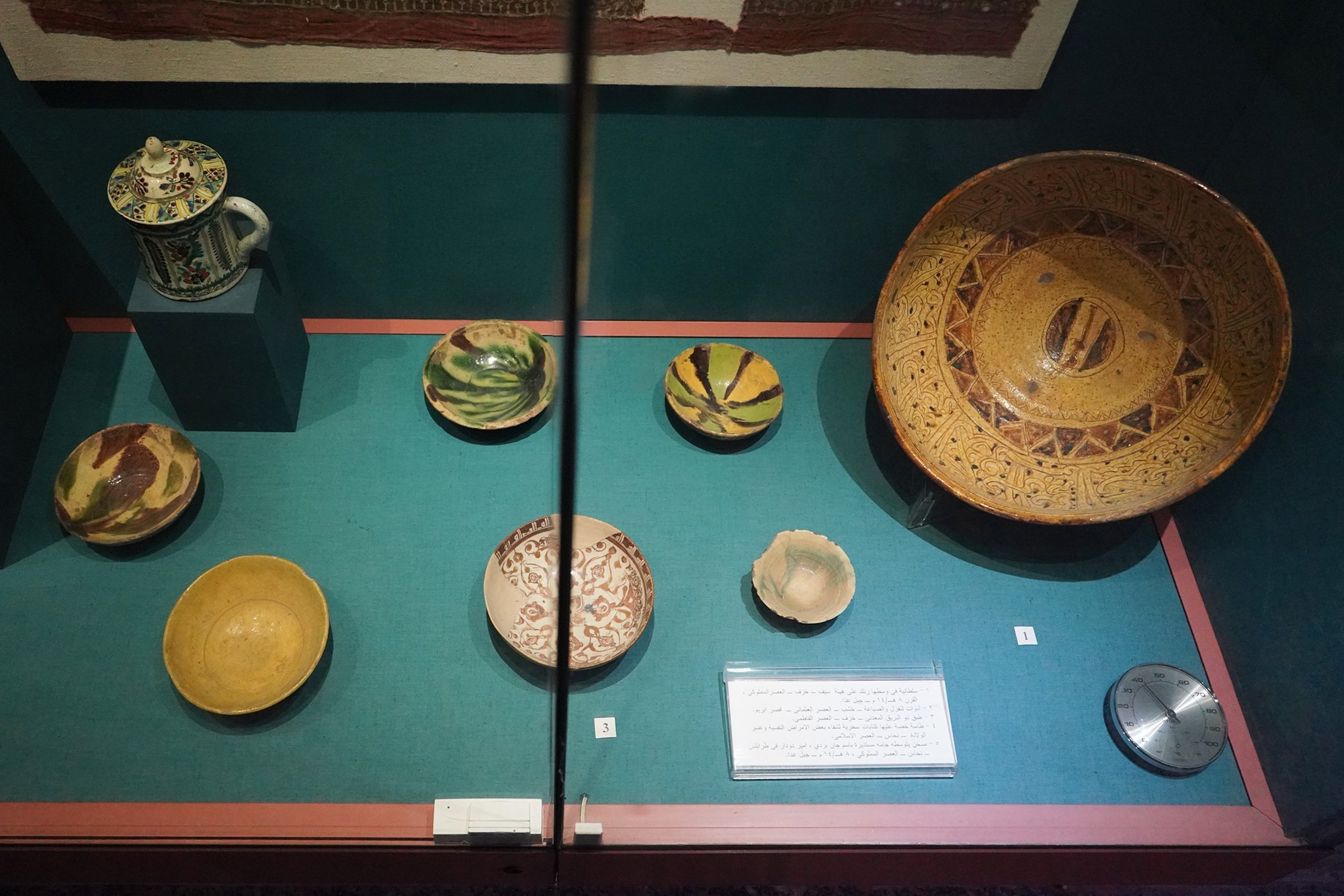
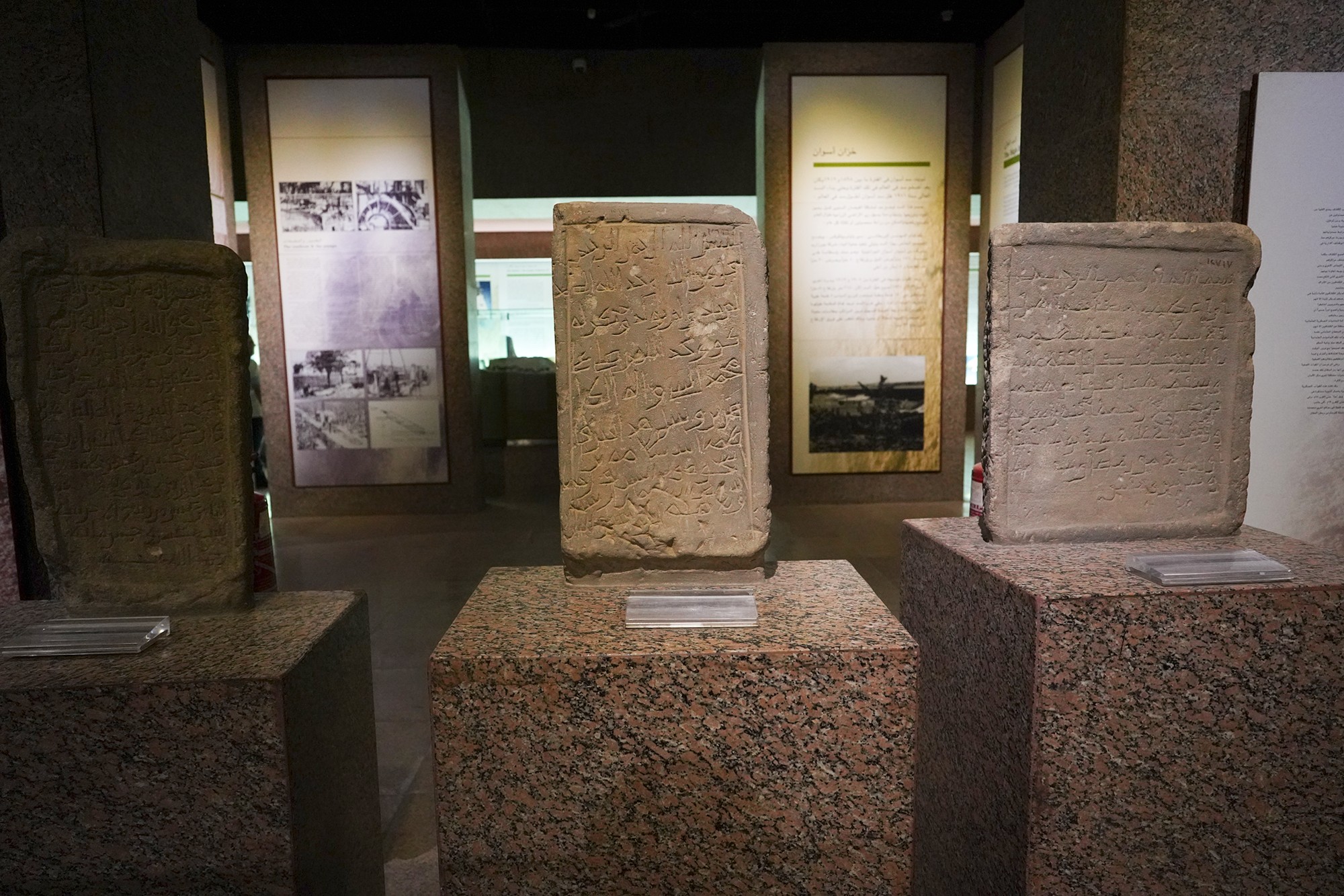
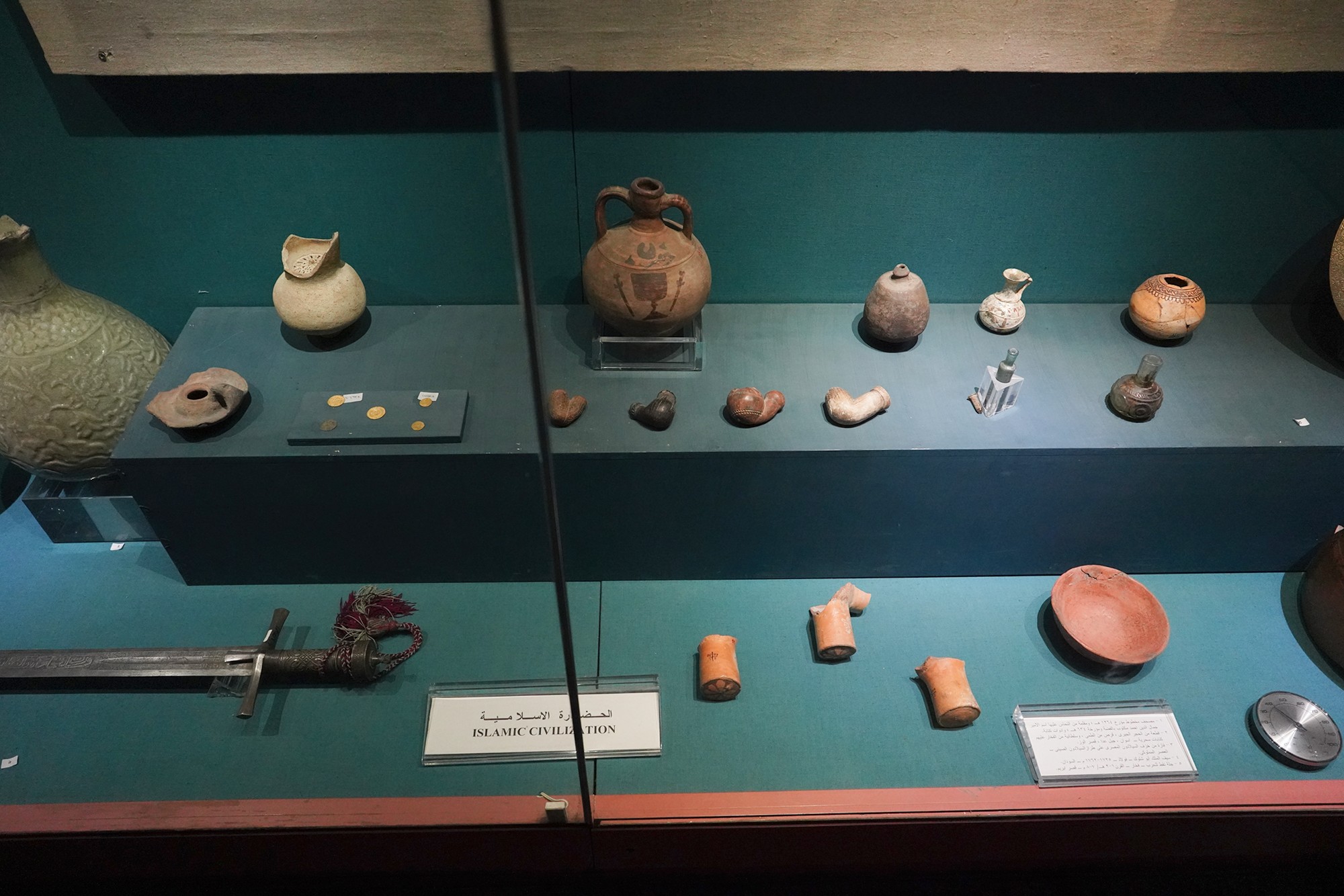








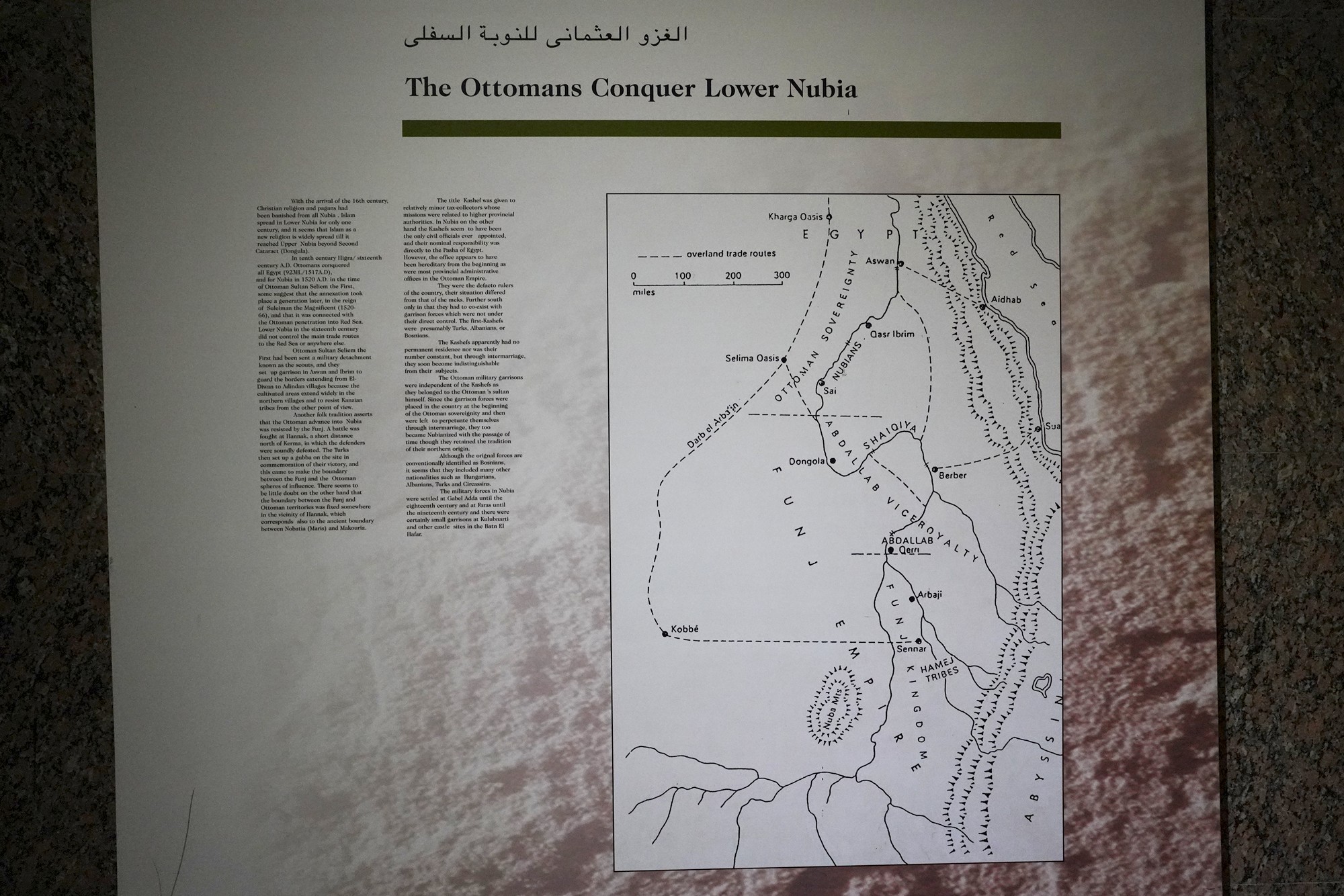




In the 19th century, the Ottoman Empire, in collaboration with Egypt, extended its influence over Sudan and Nubia. This period saw increased contact with European powers, including British and Egyptian control over the region.
While the High Dam was being built, these were the countries that helped save the Egyptian temples that would have been lost due to the flooding.



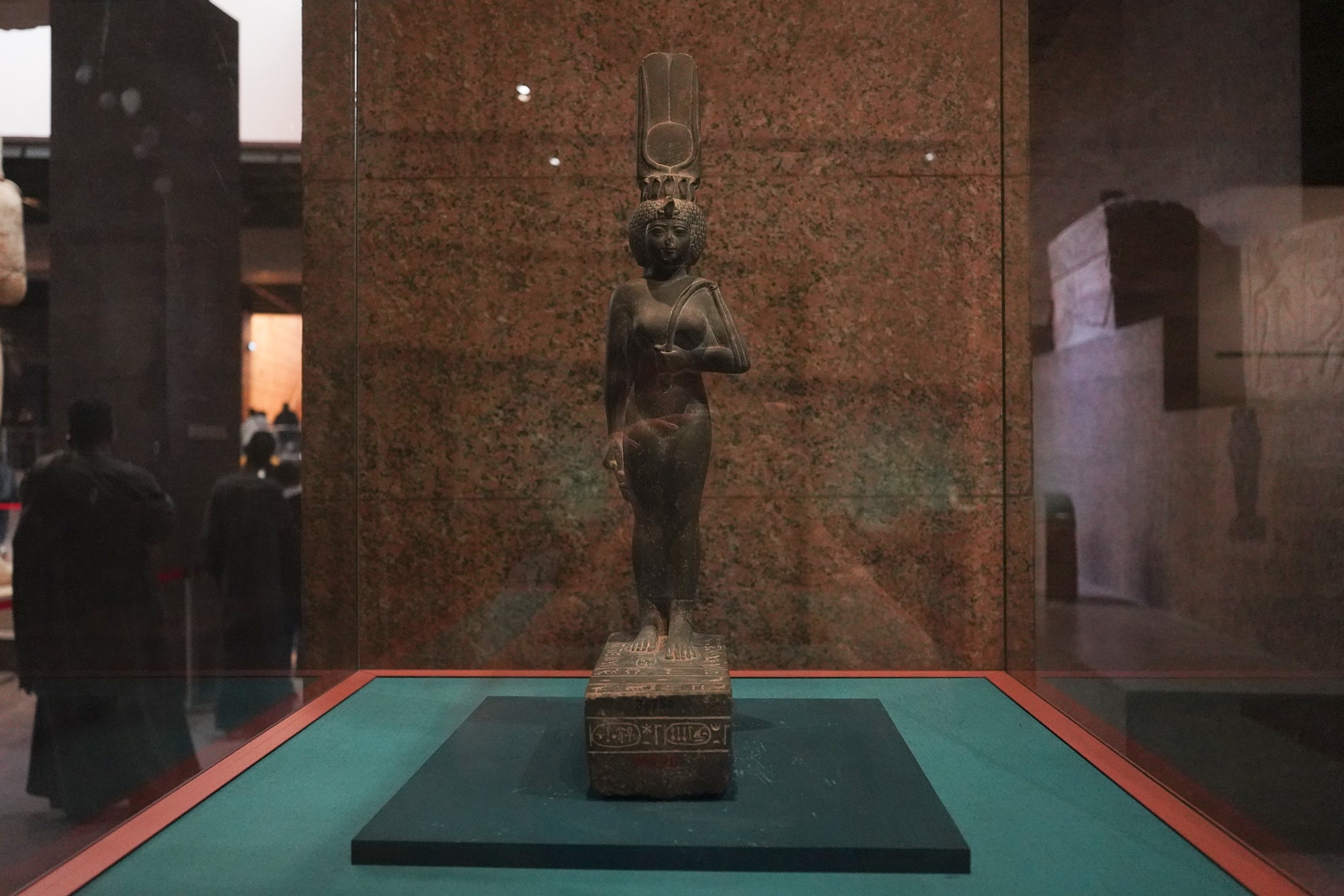
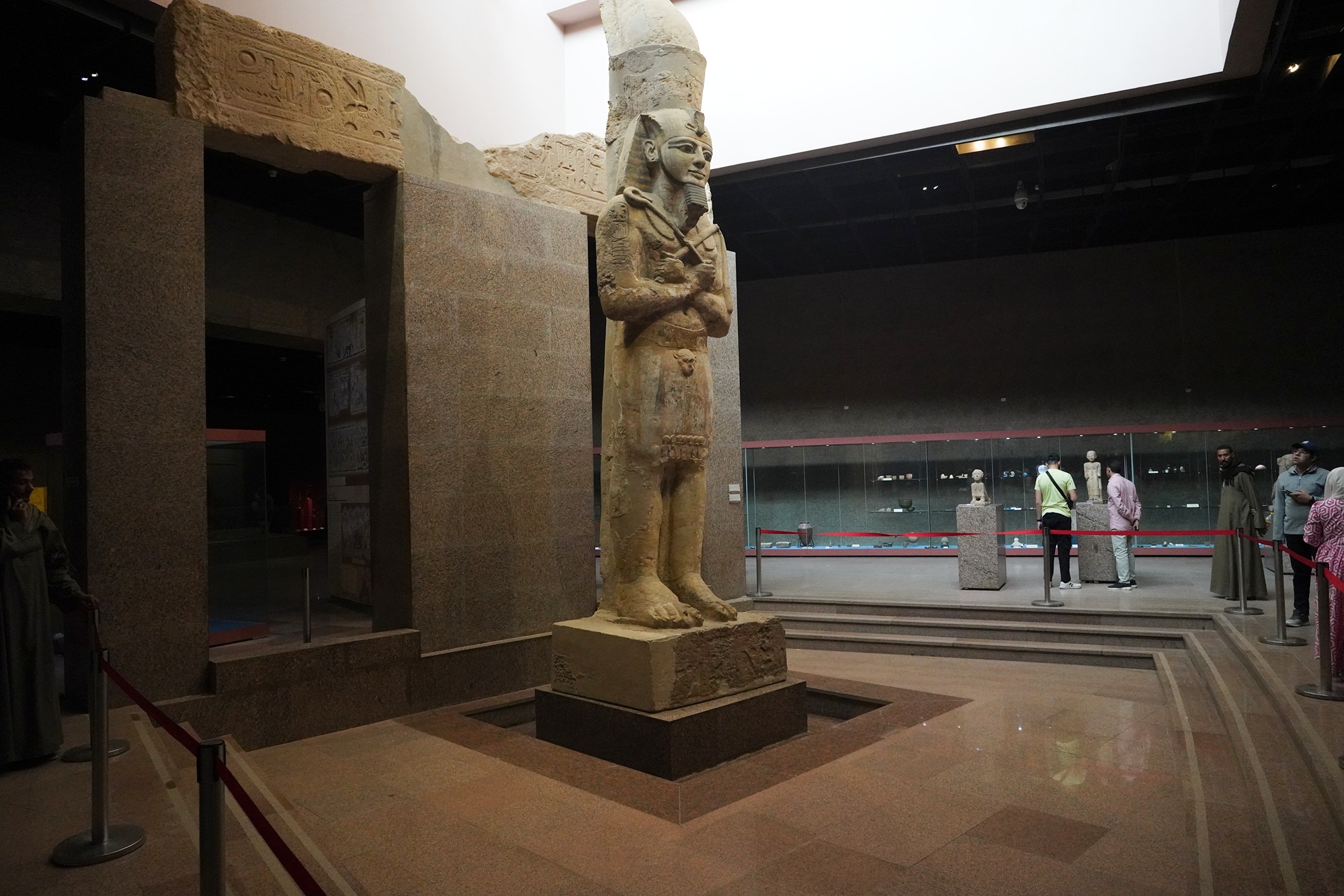
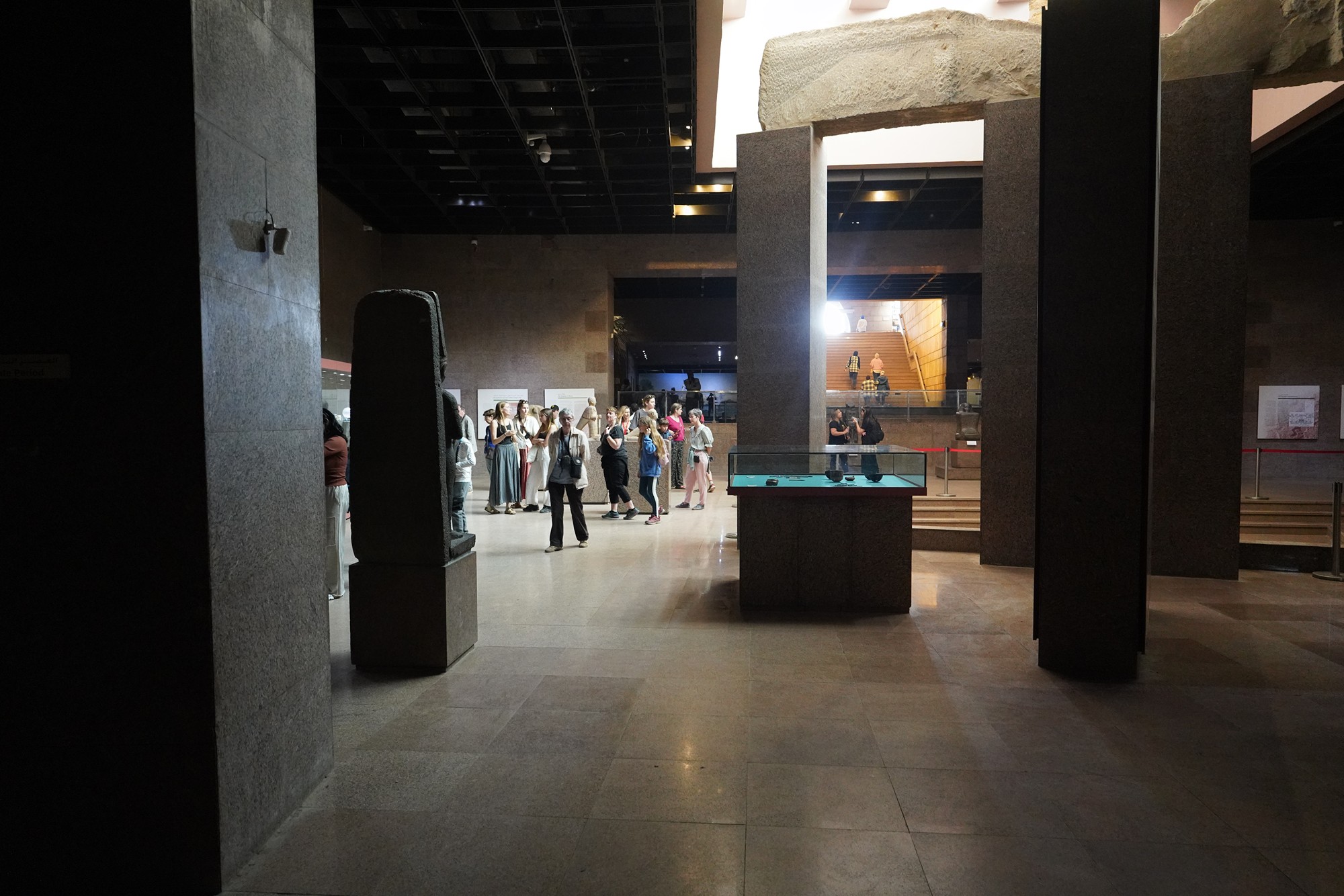
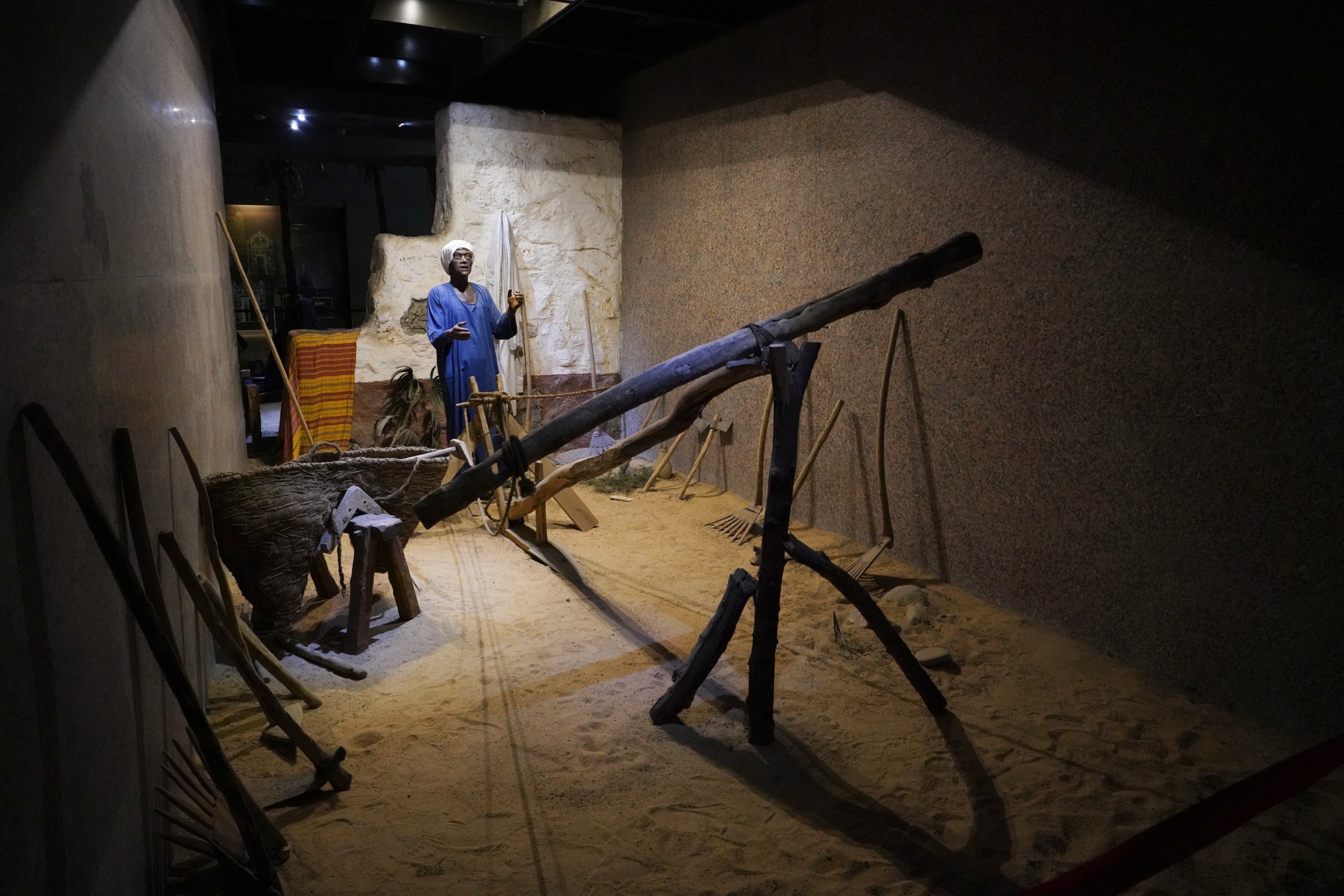
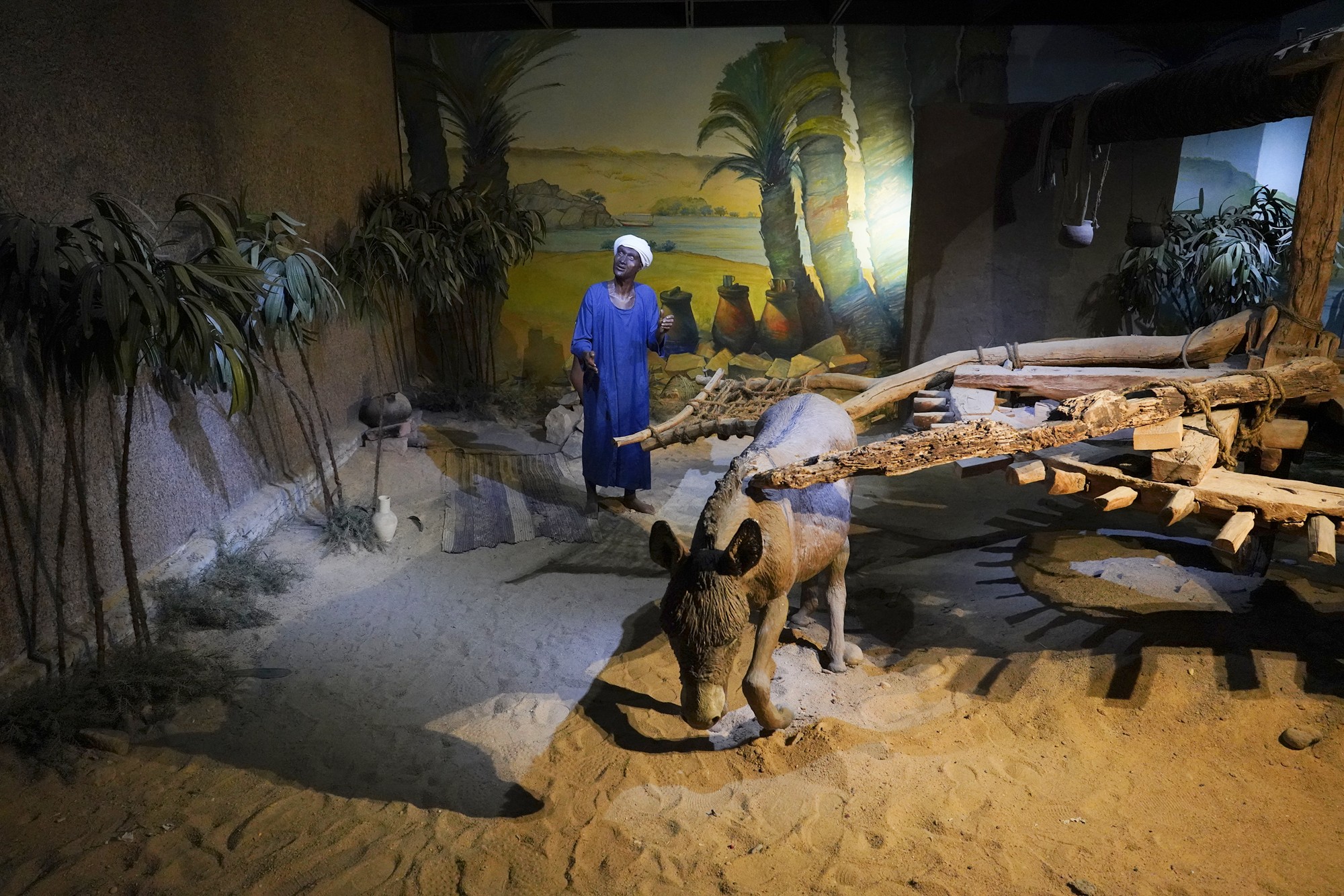
Egypt’s ancient life depicted with figures





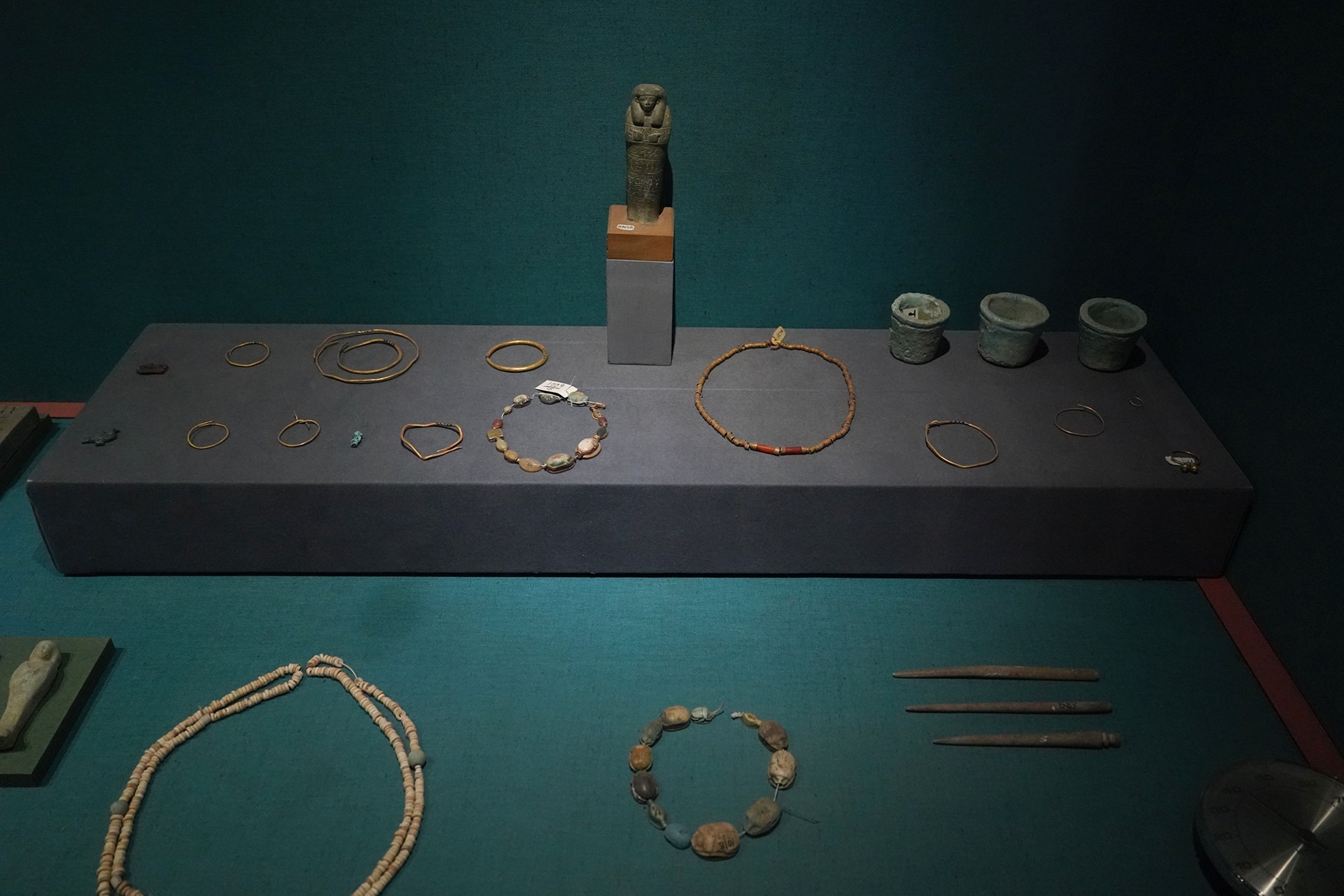
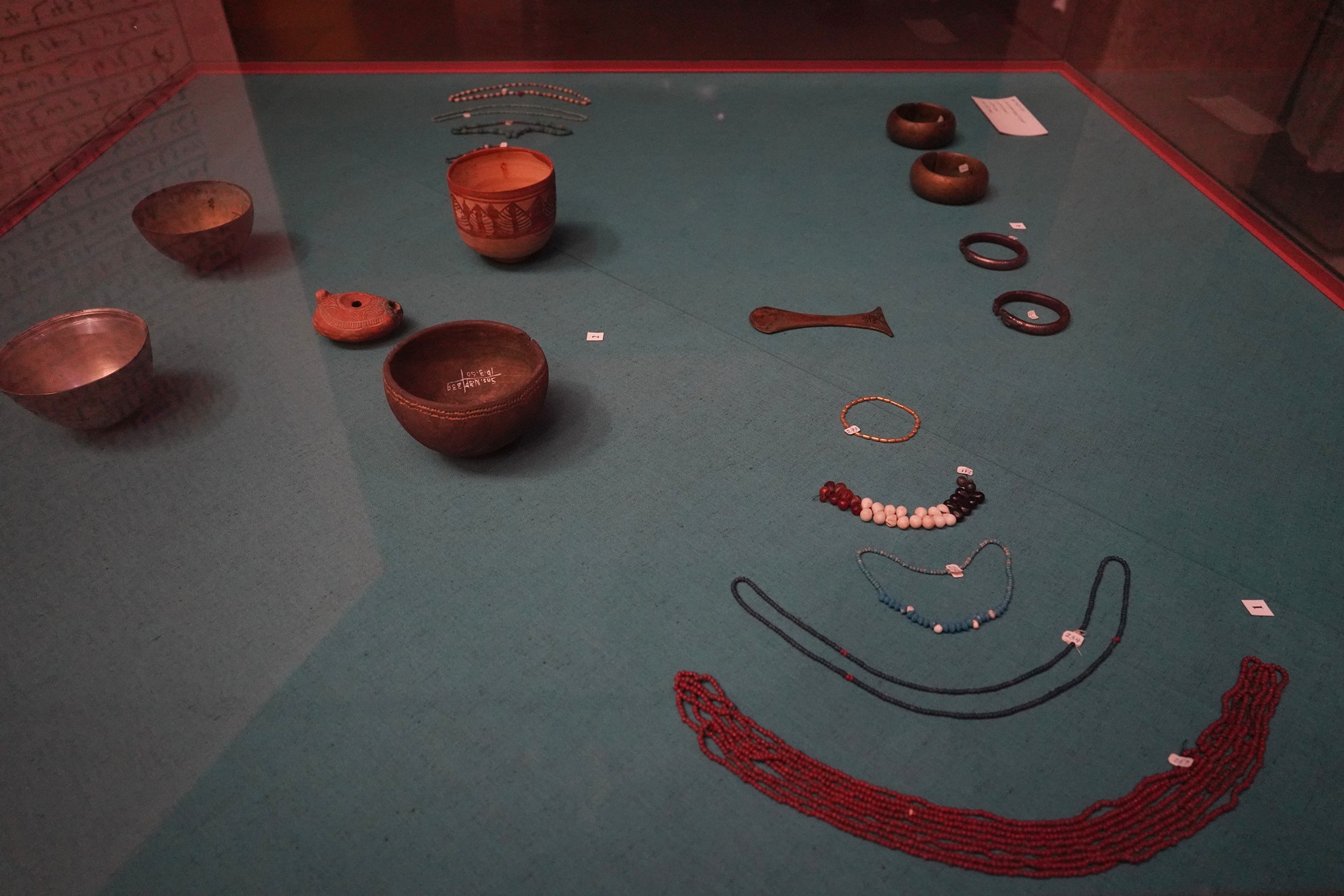
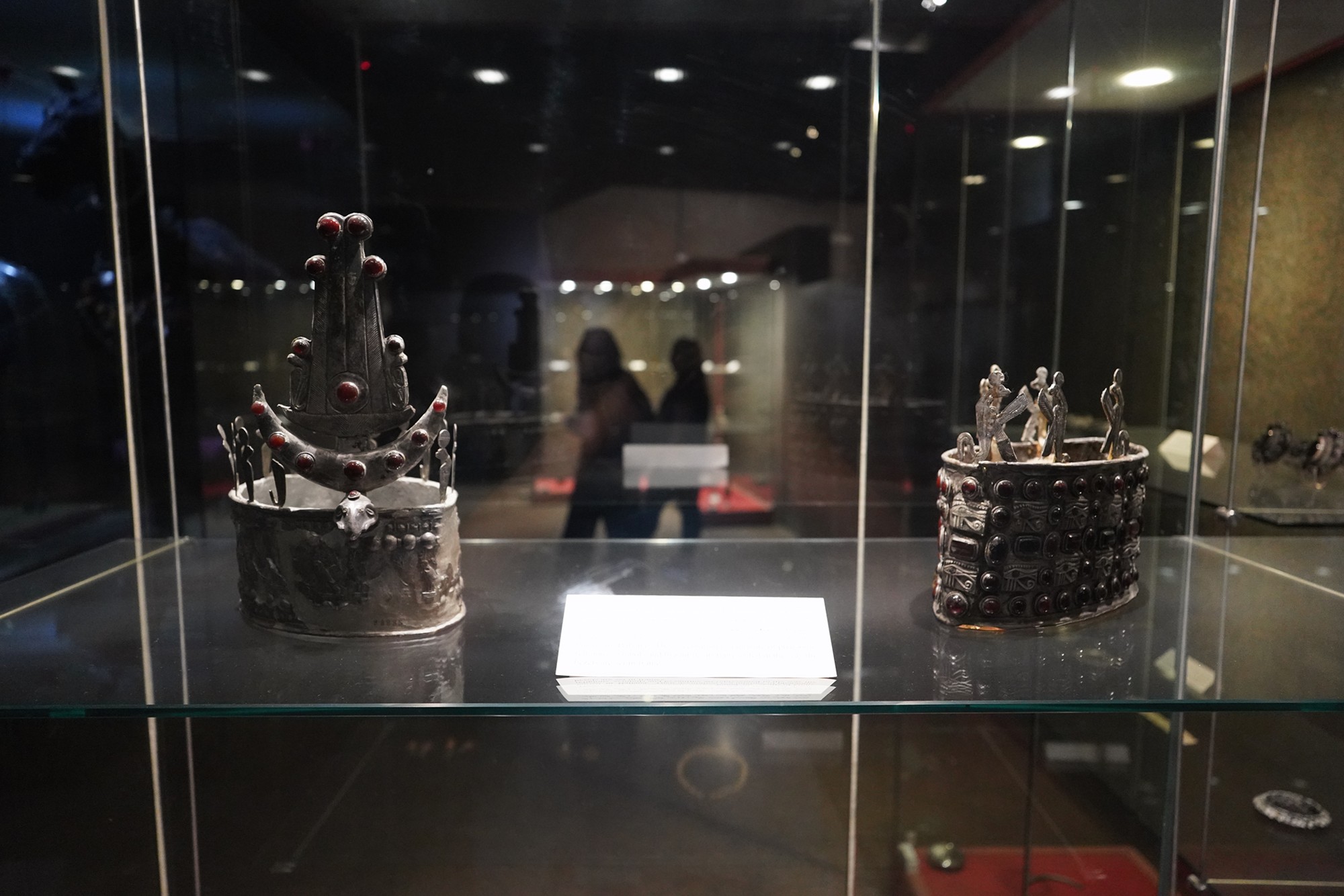
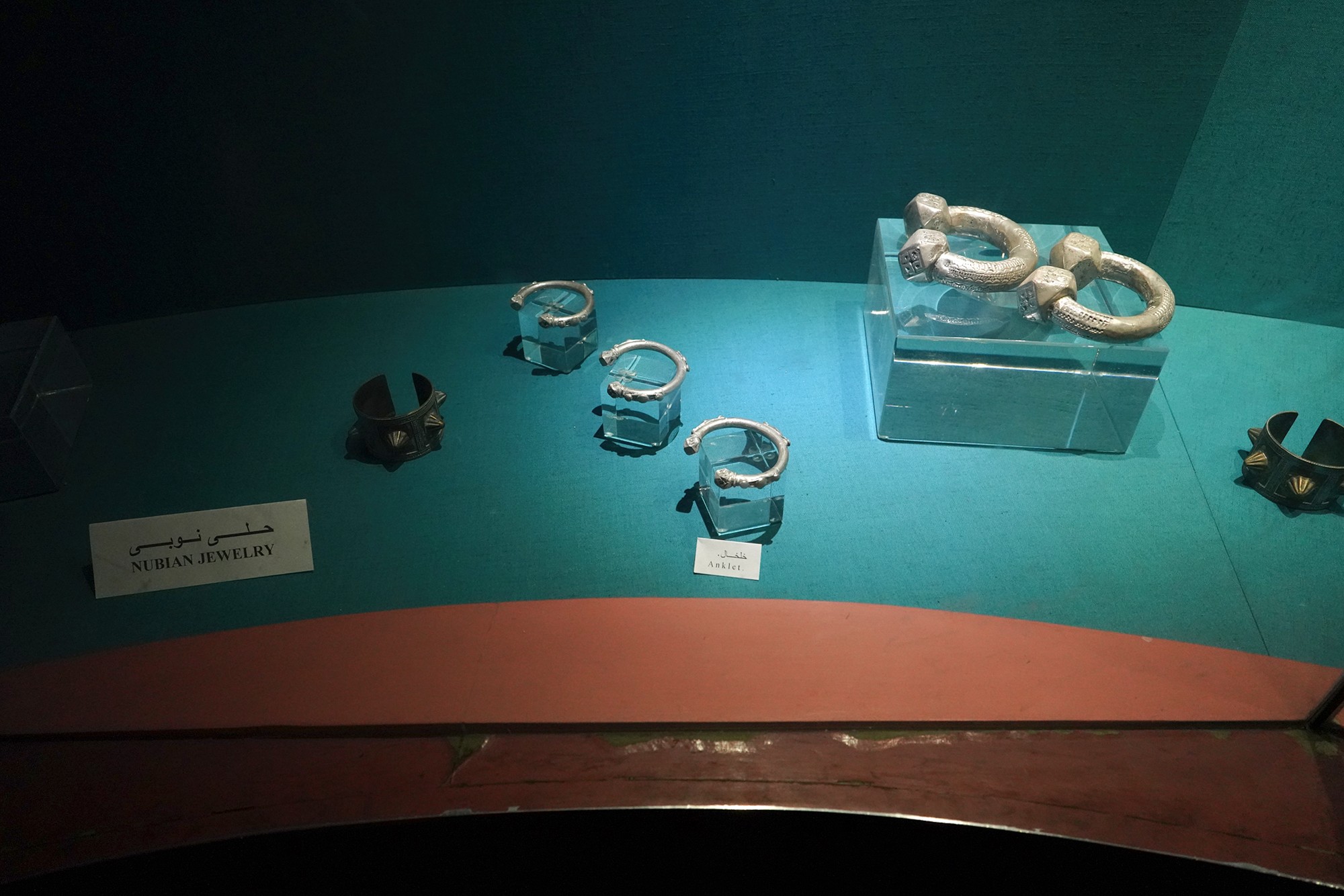
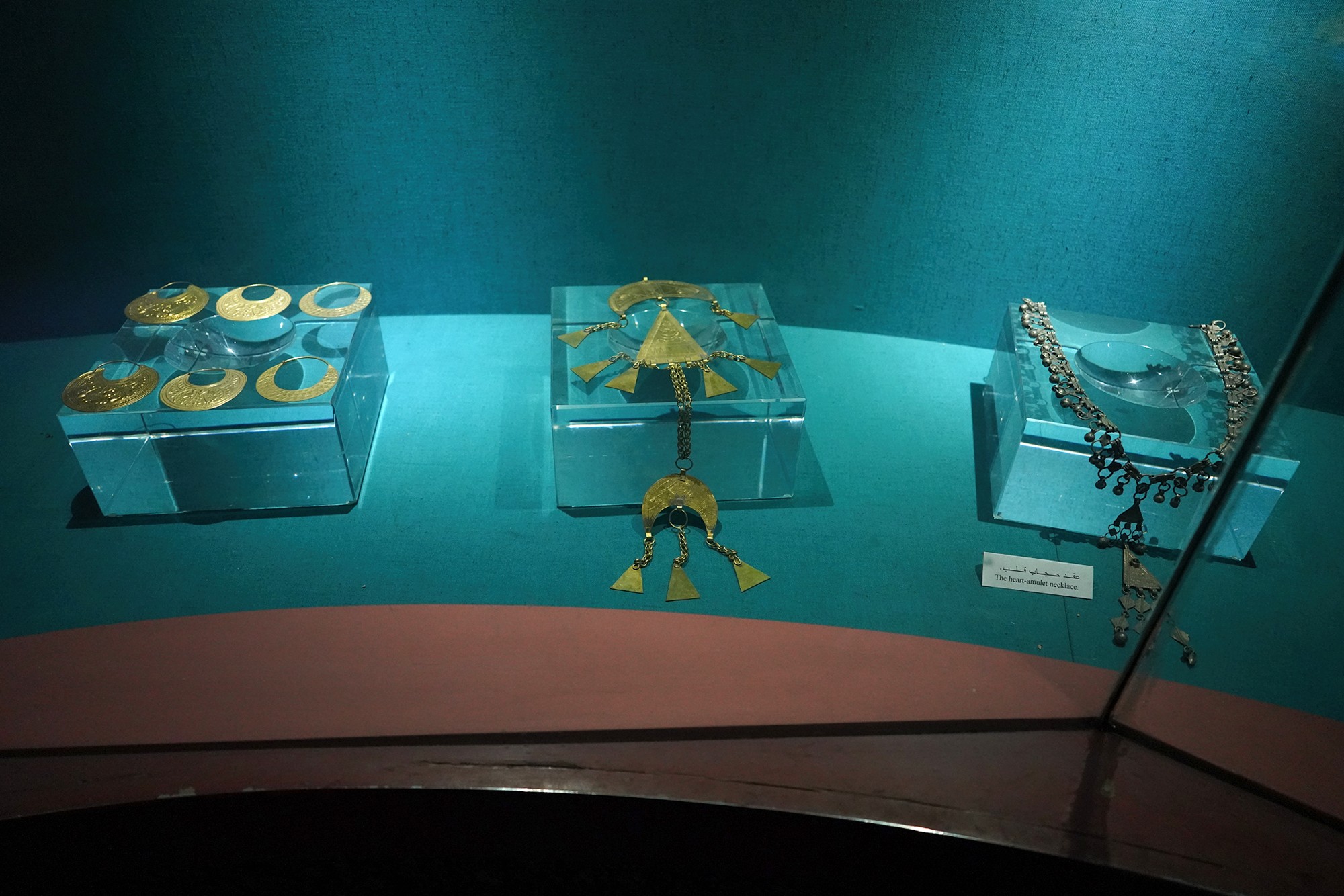
Nubain Jewels




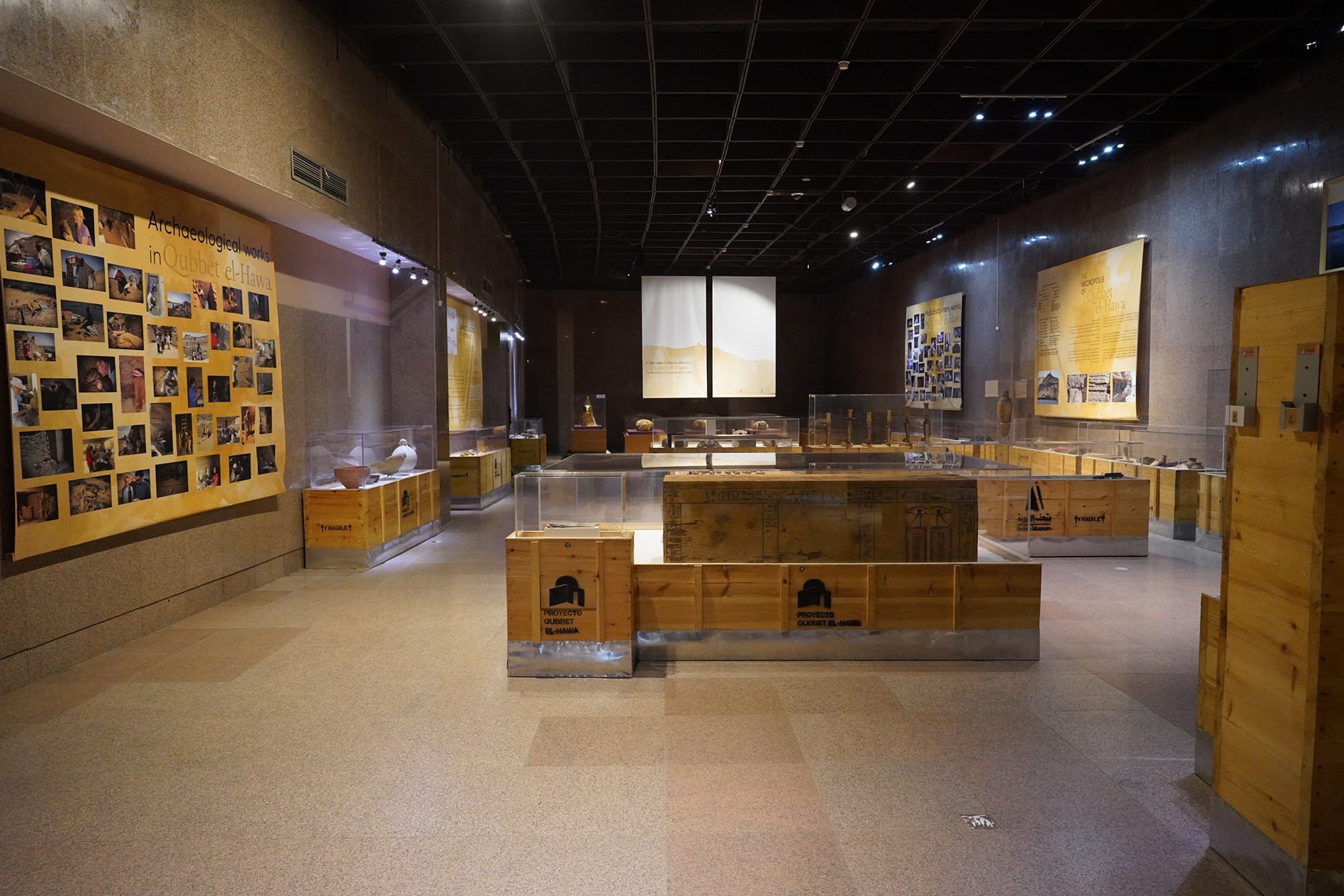
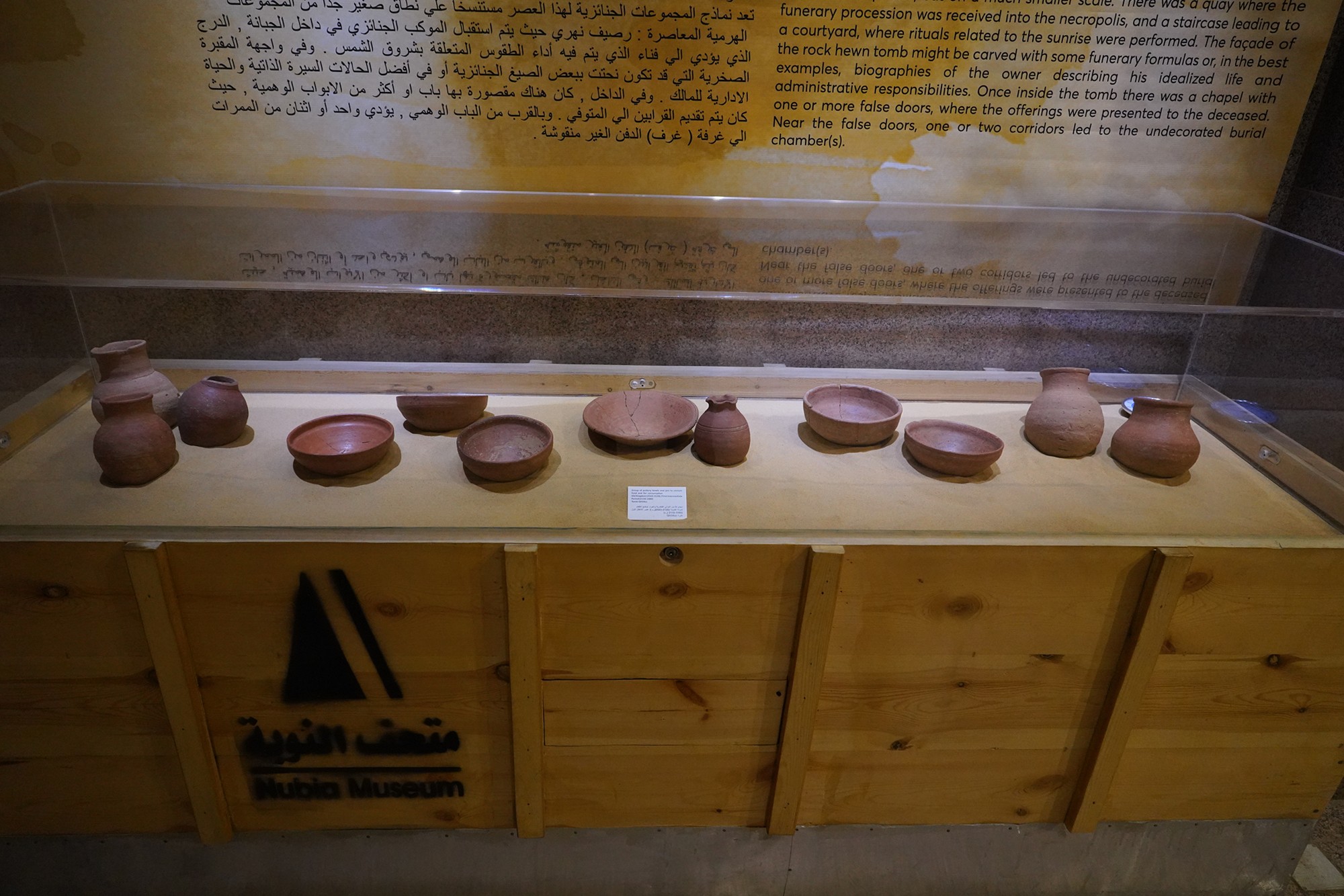
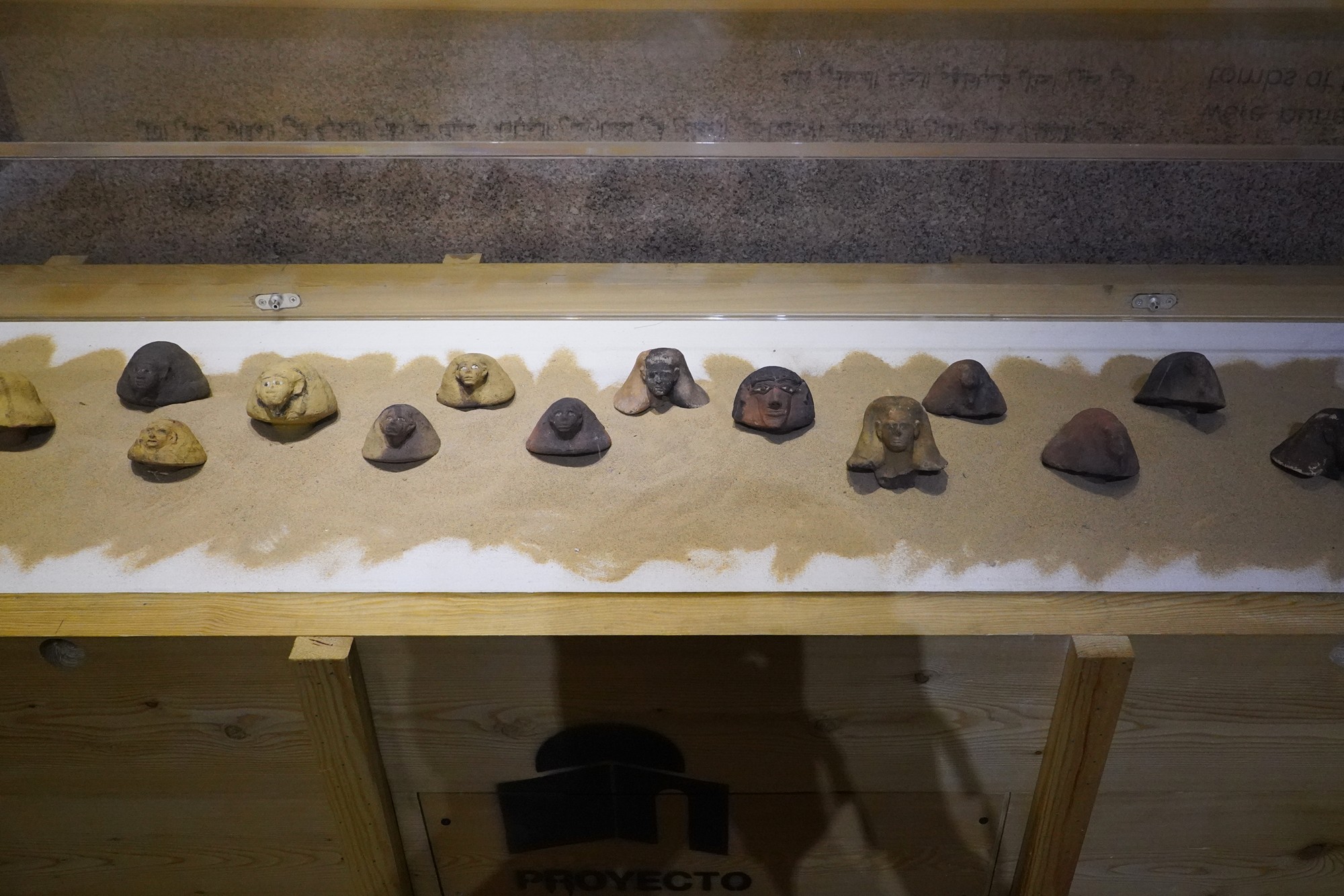
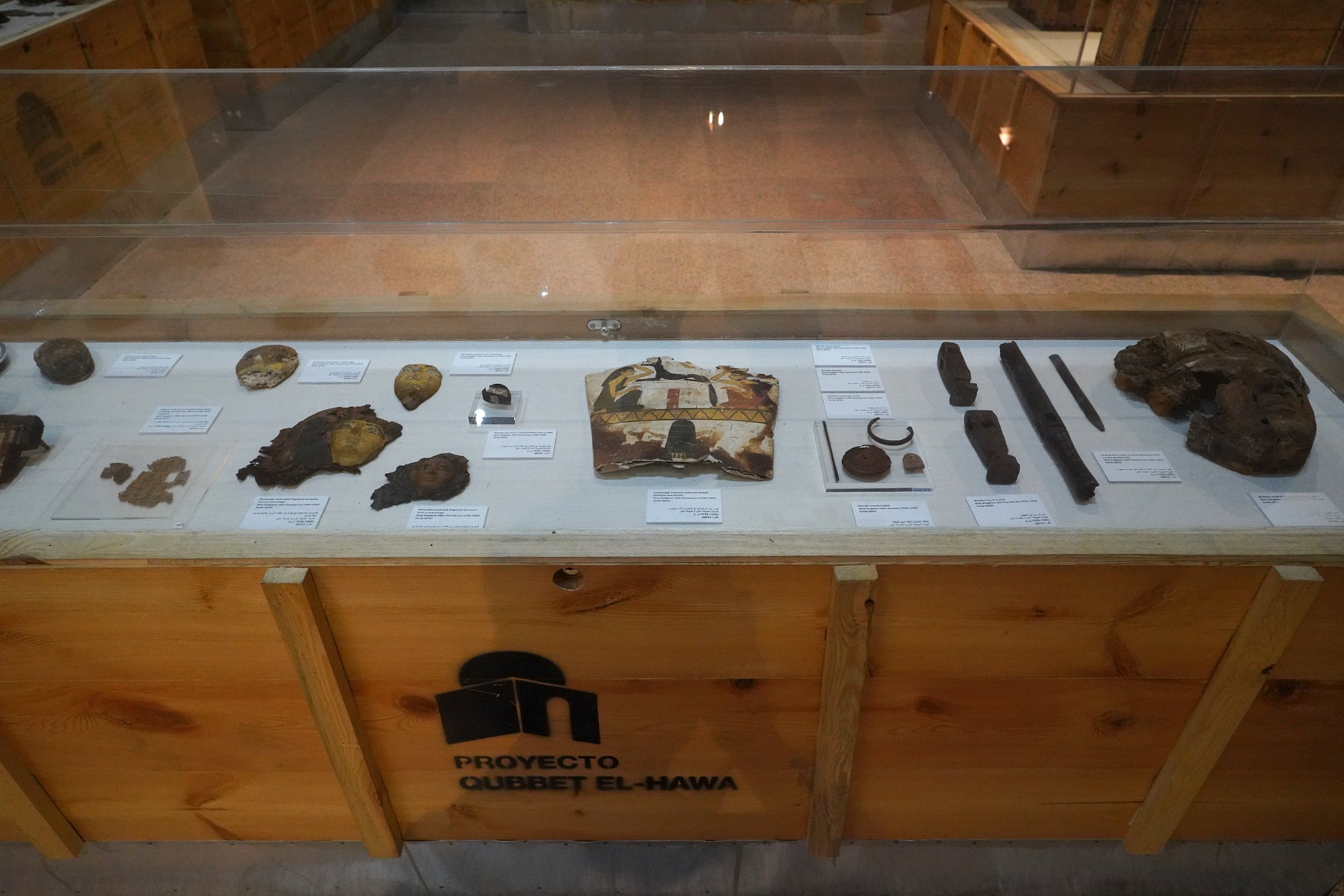
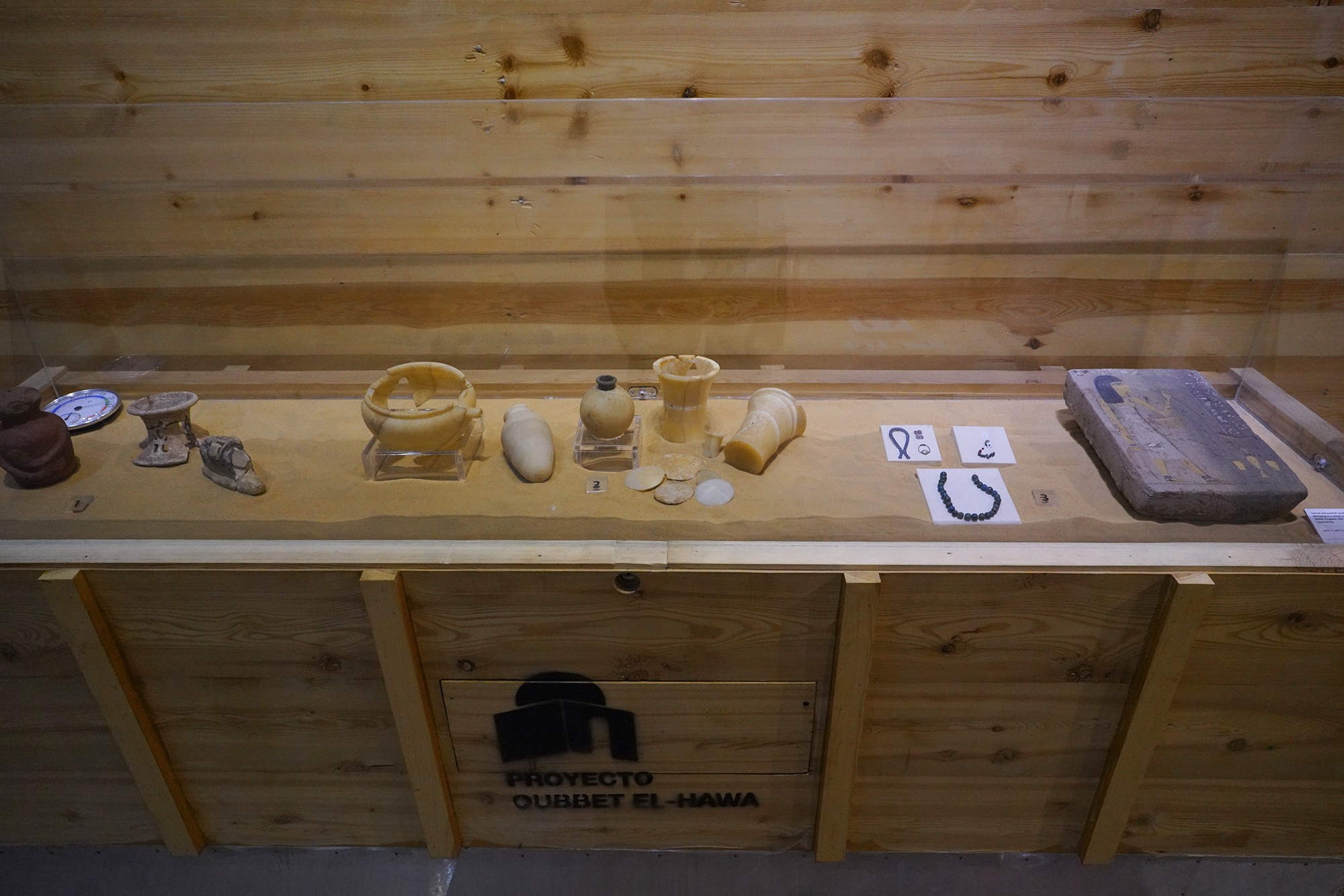
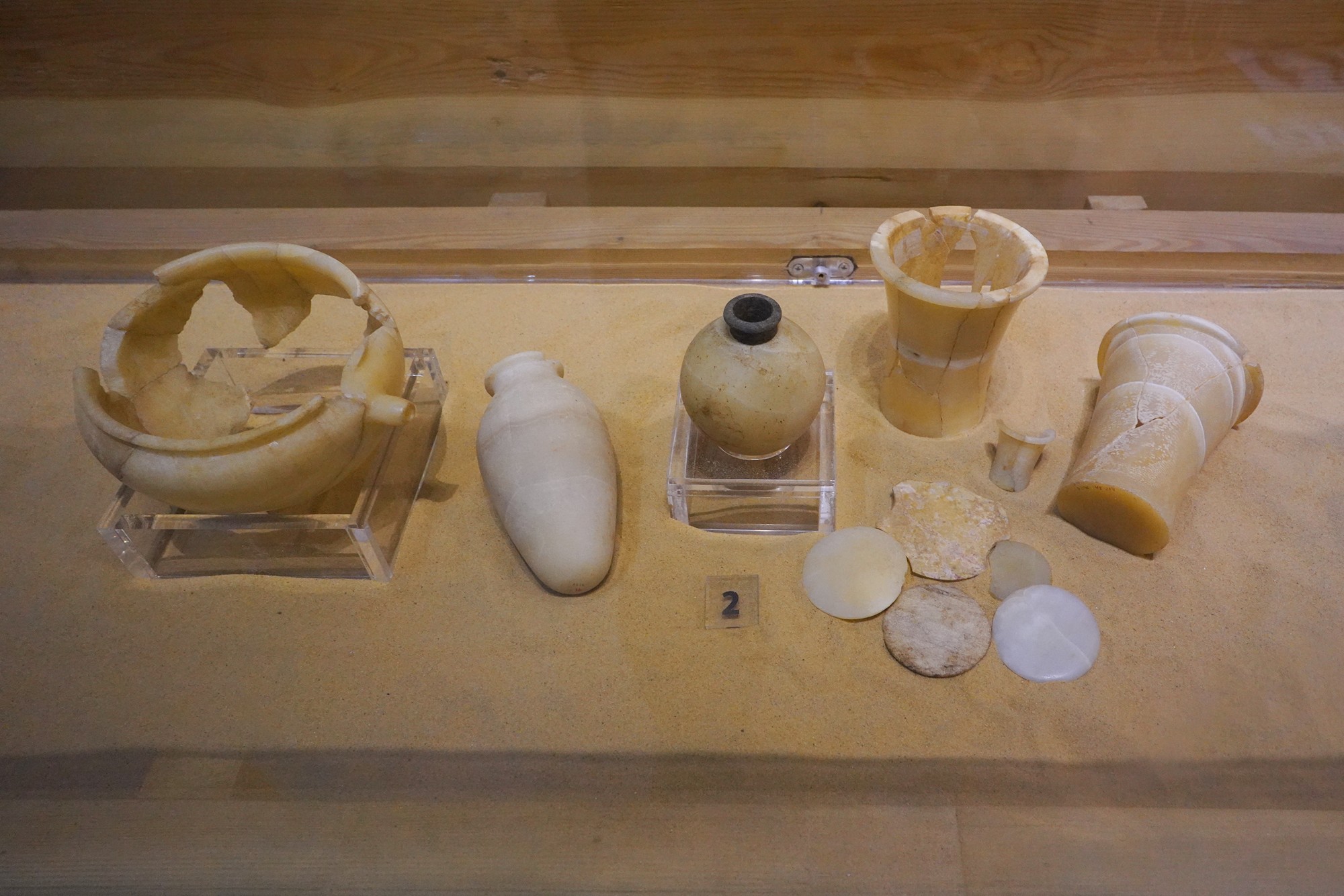
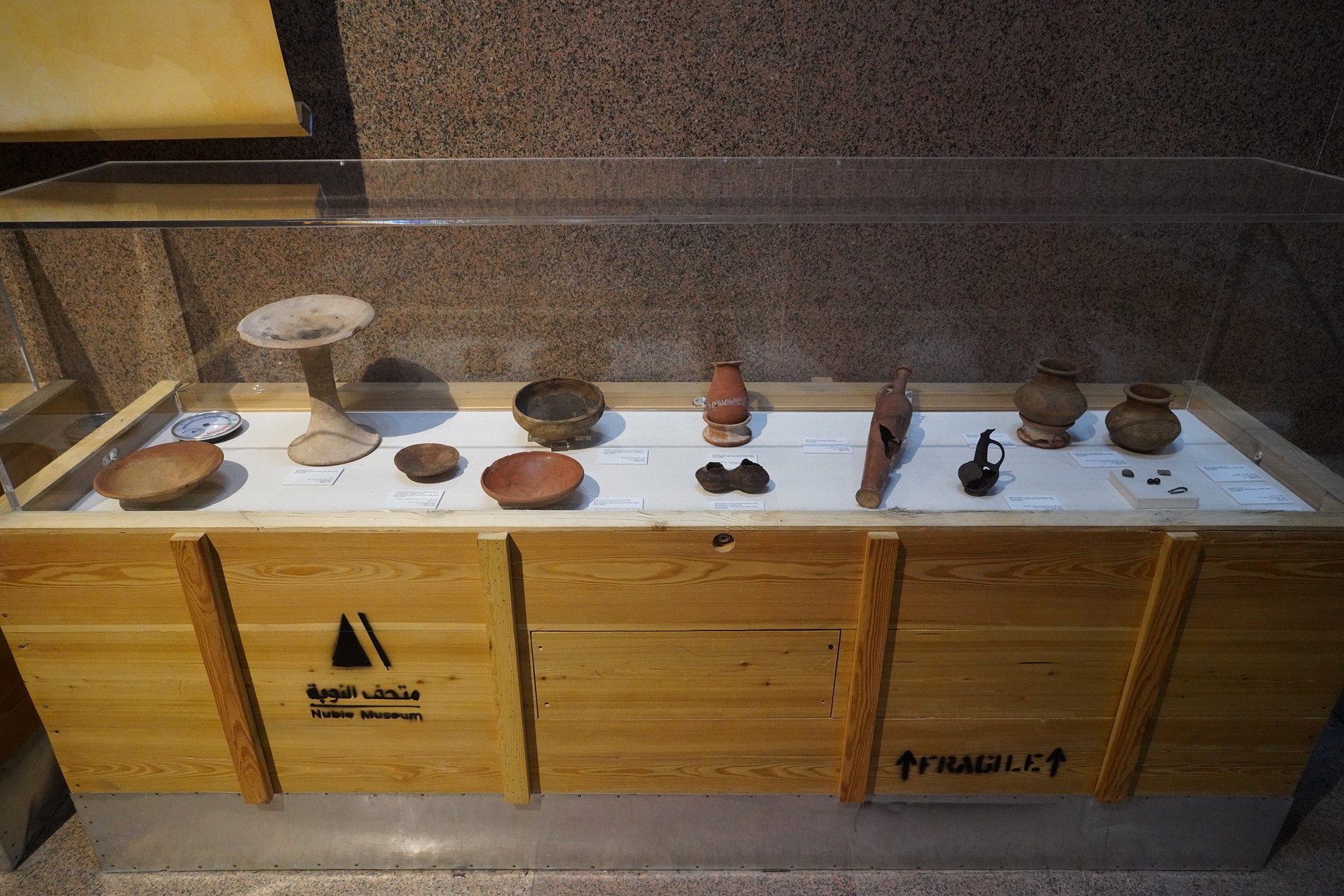
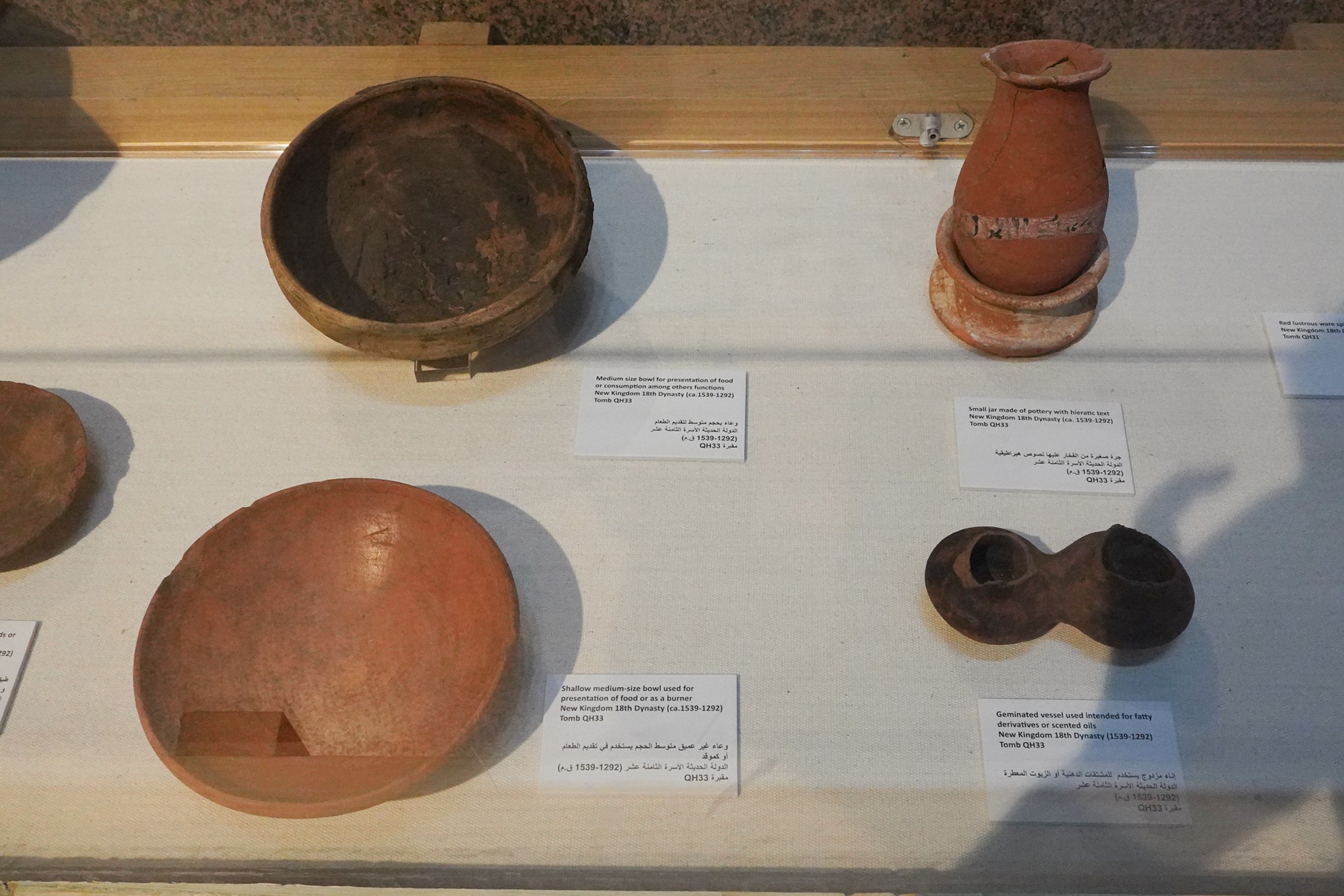
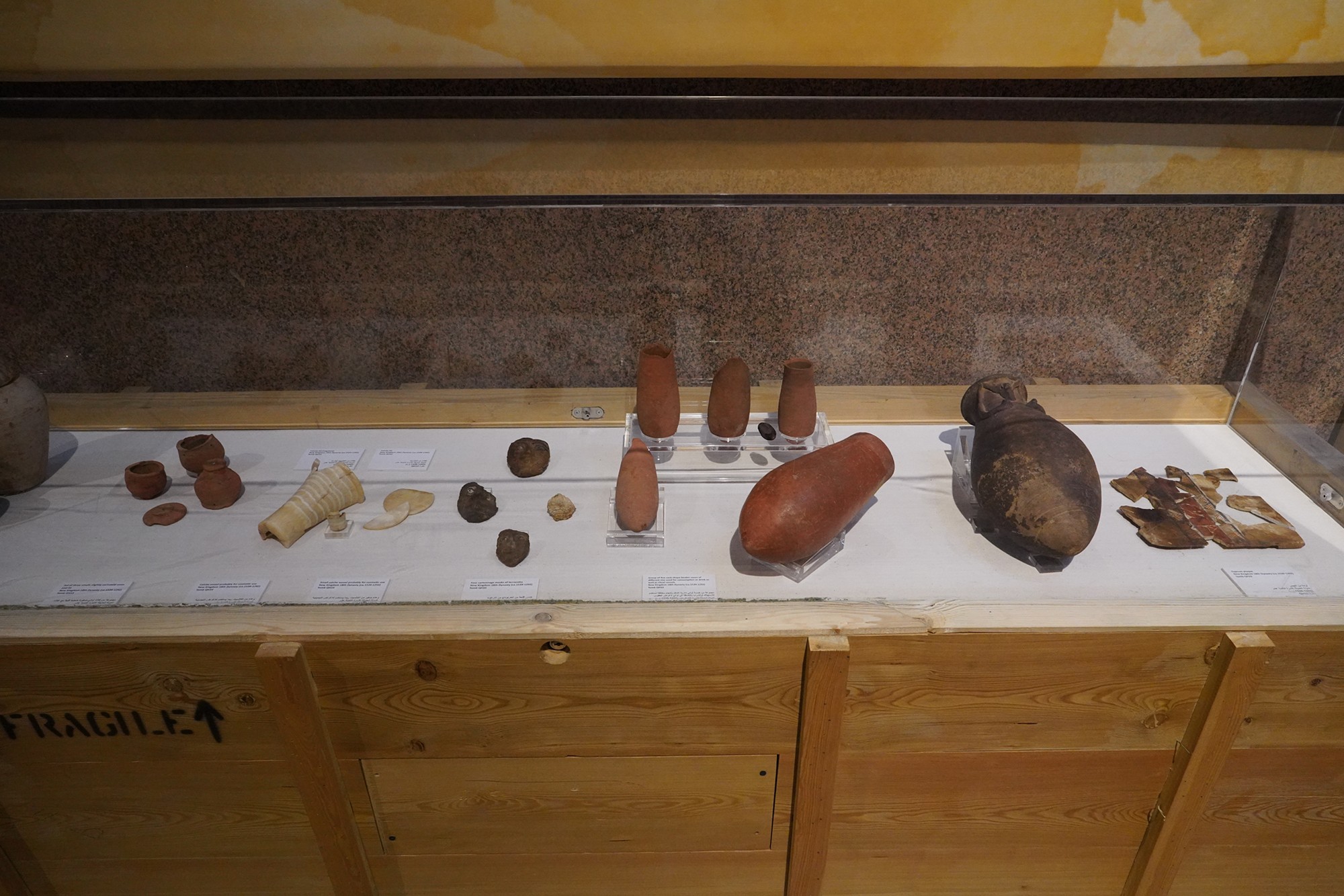
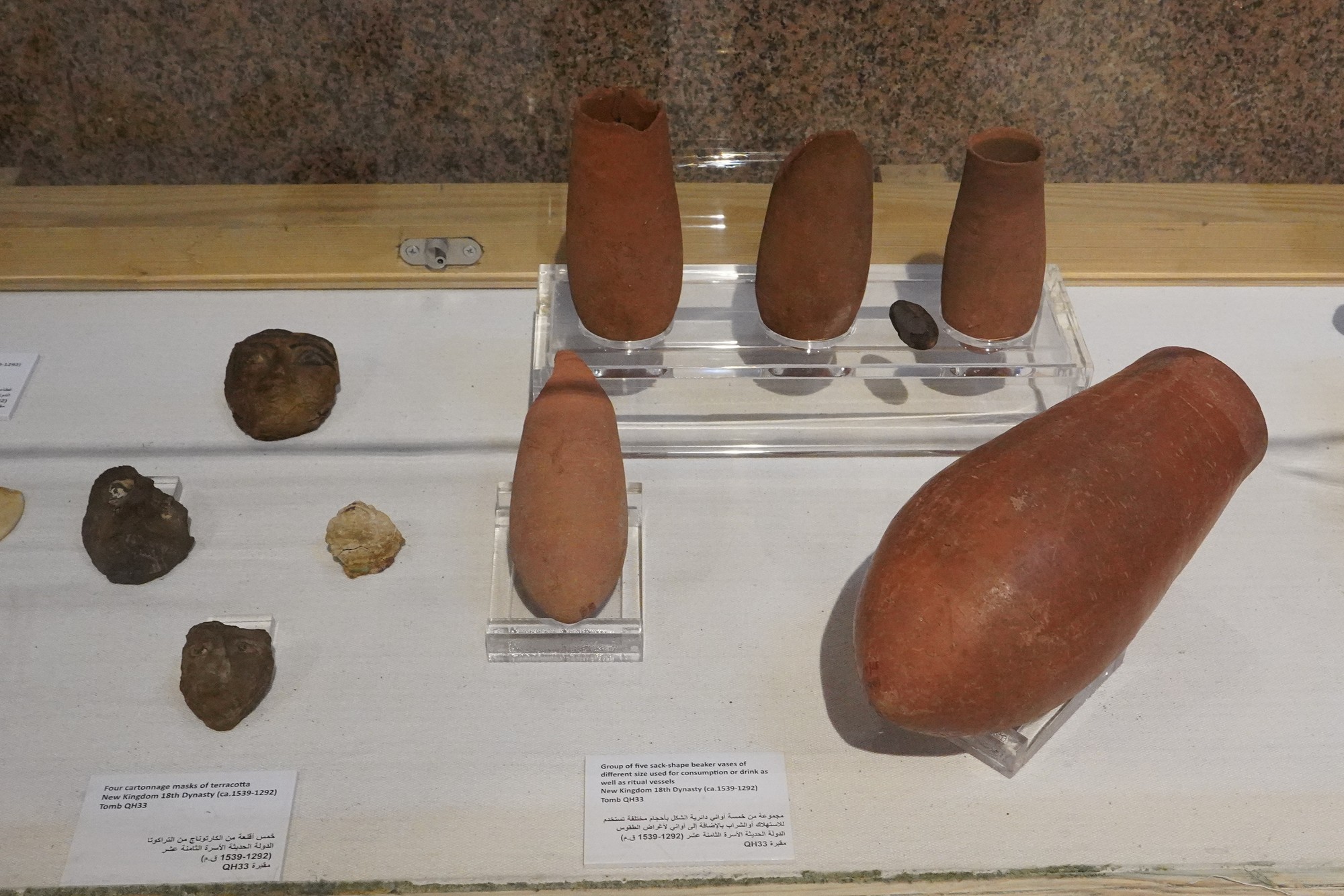
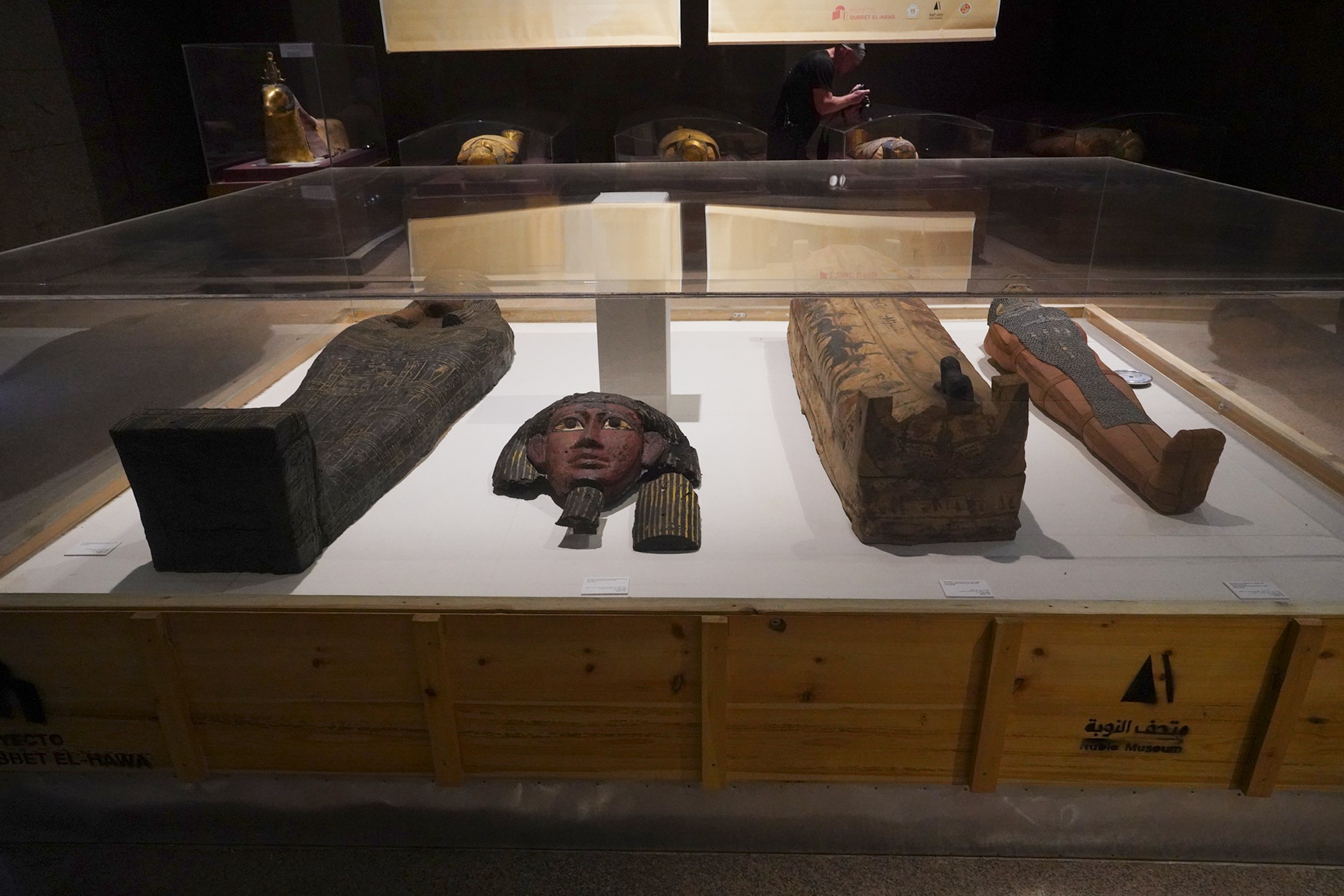
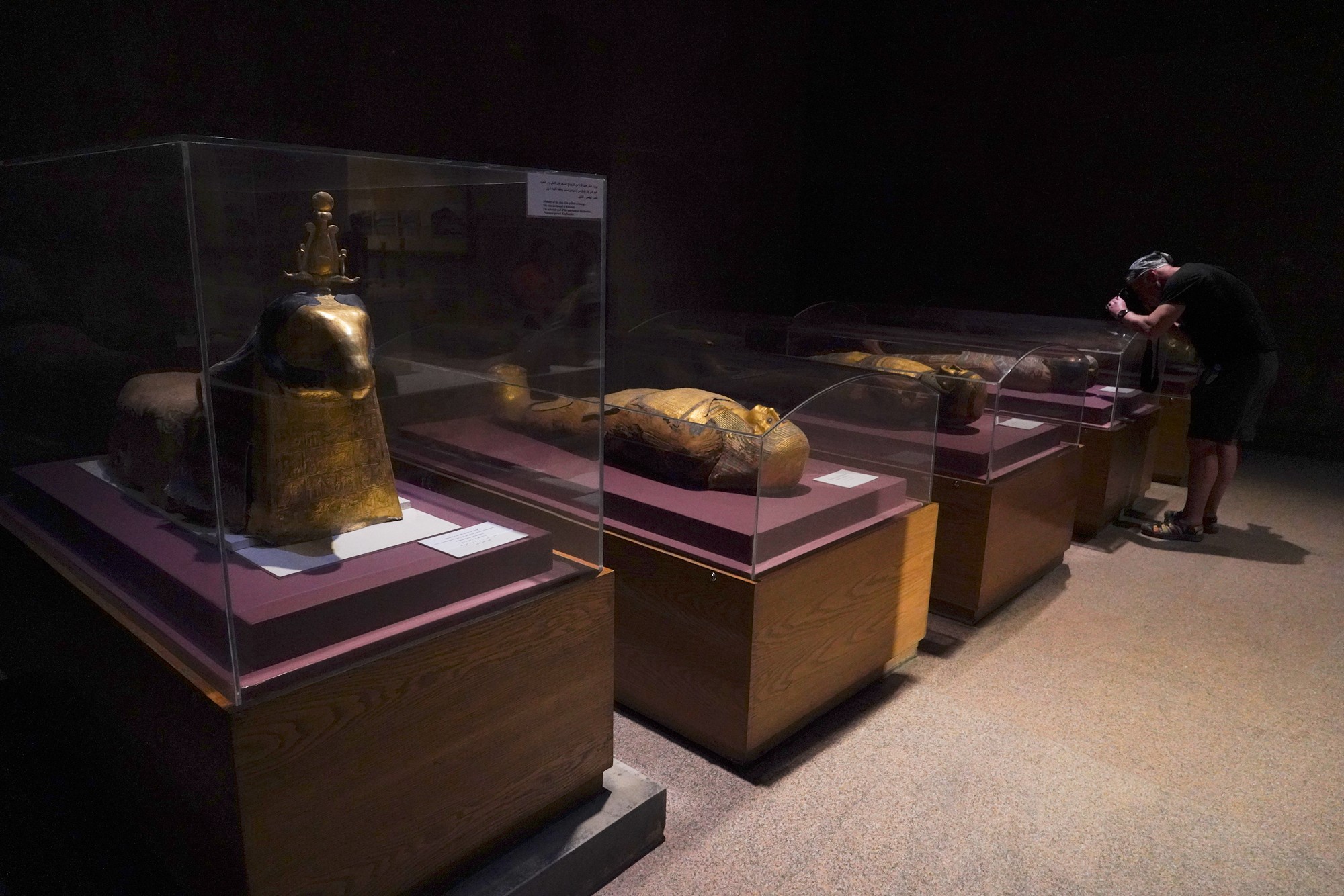
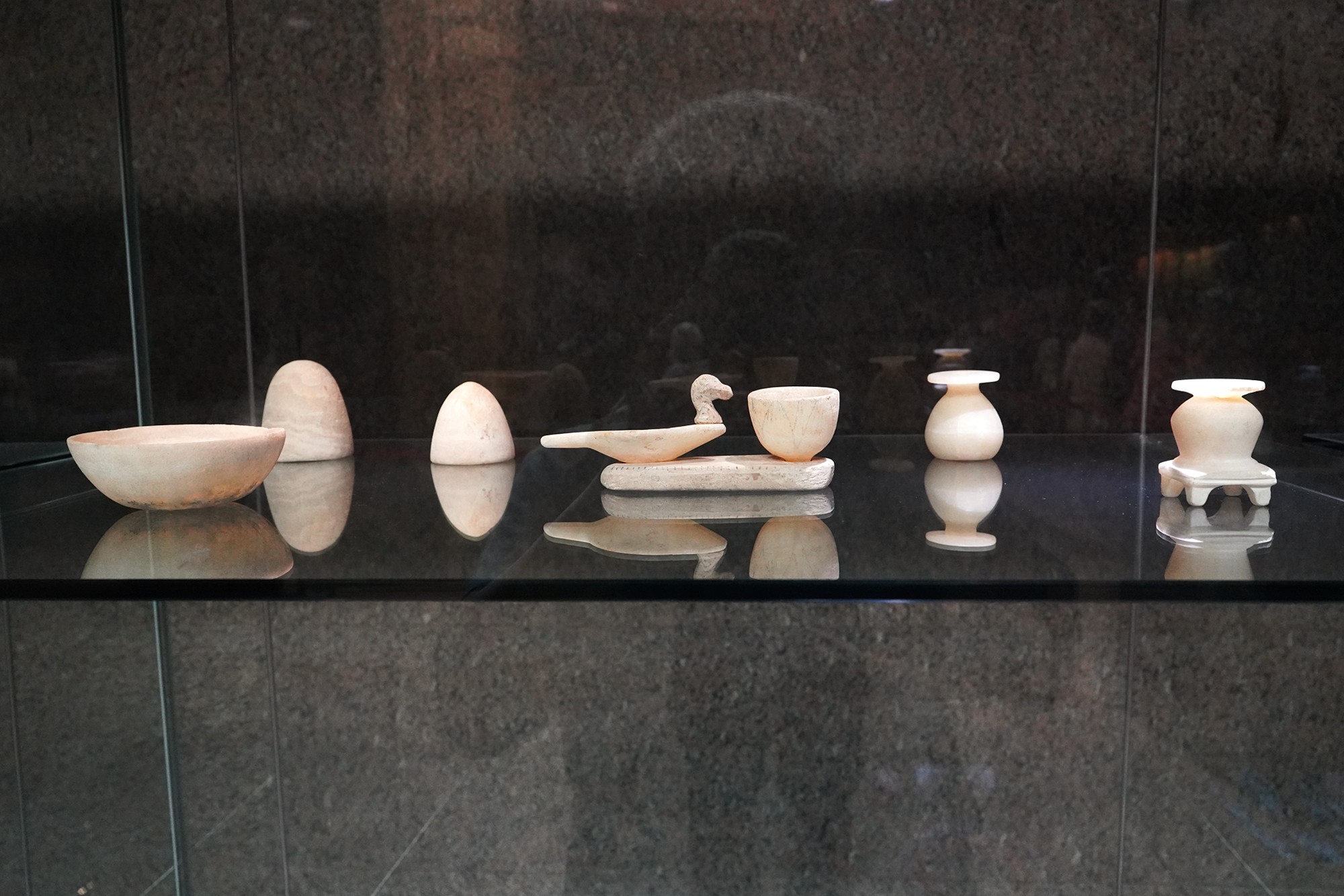
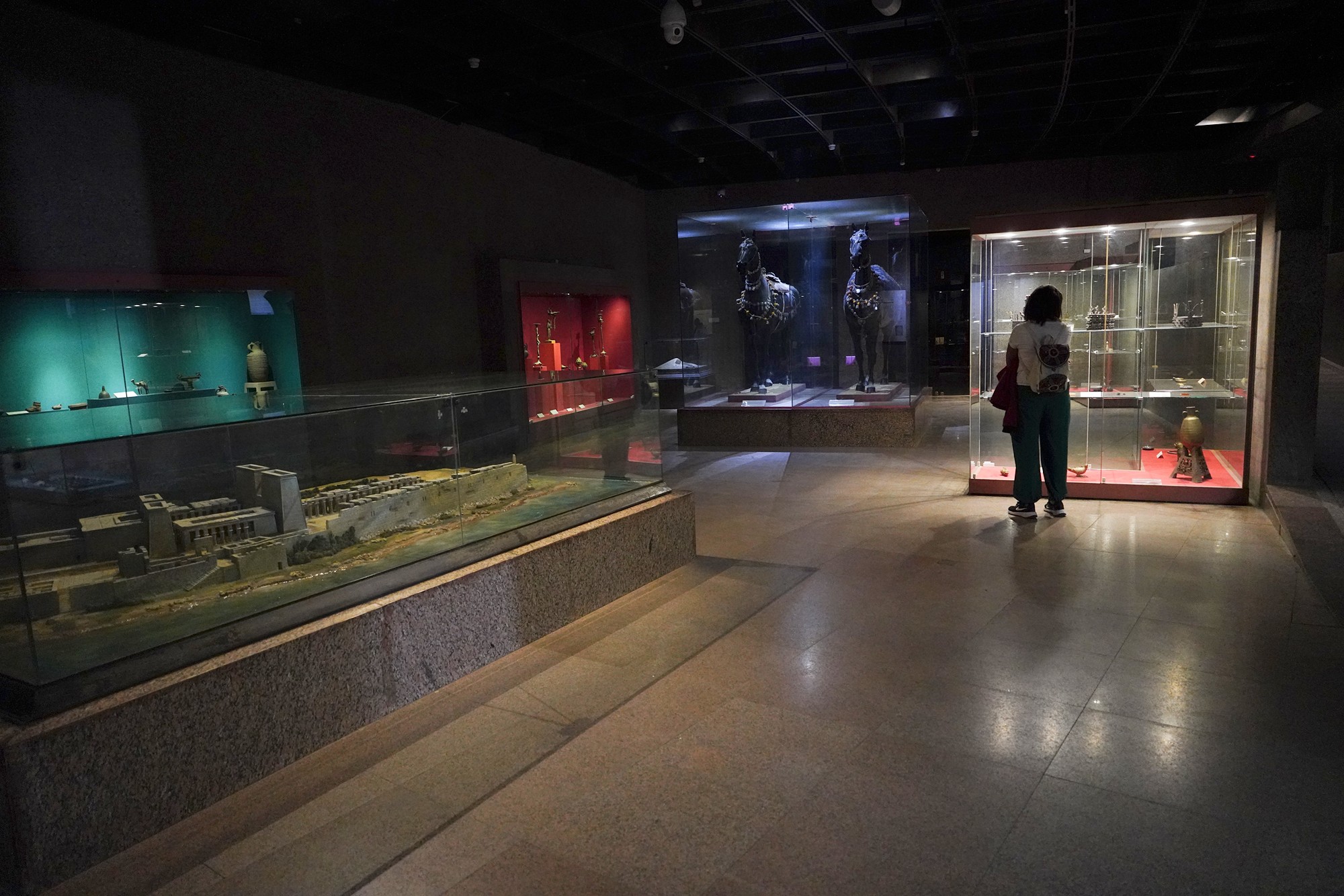
Special Exhibition showing artifacts found in recent excavation






























